Blueprint of Machine’s brain
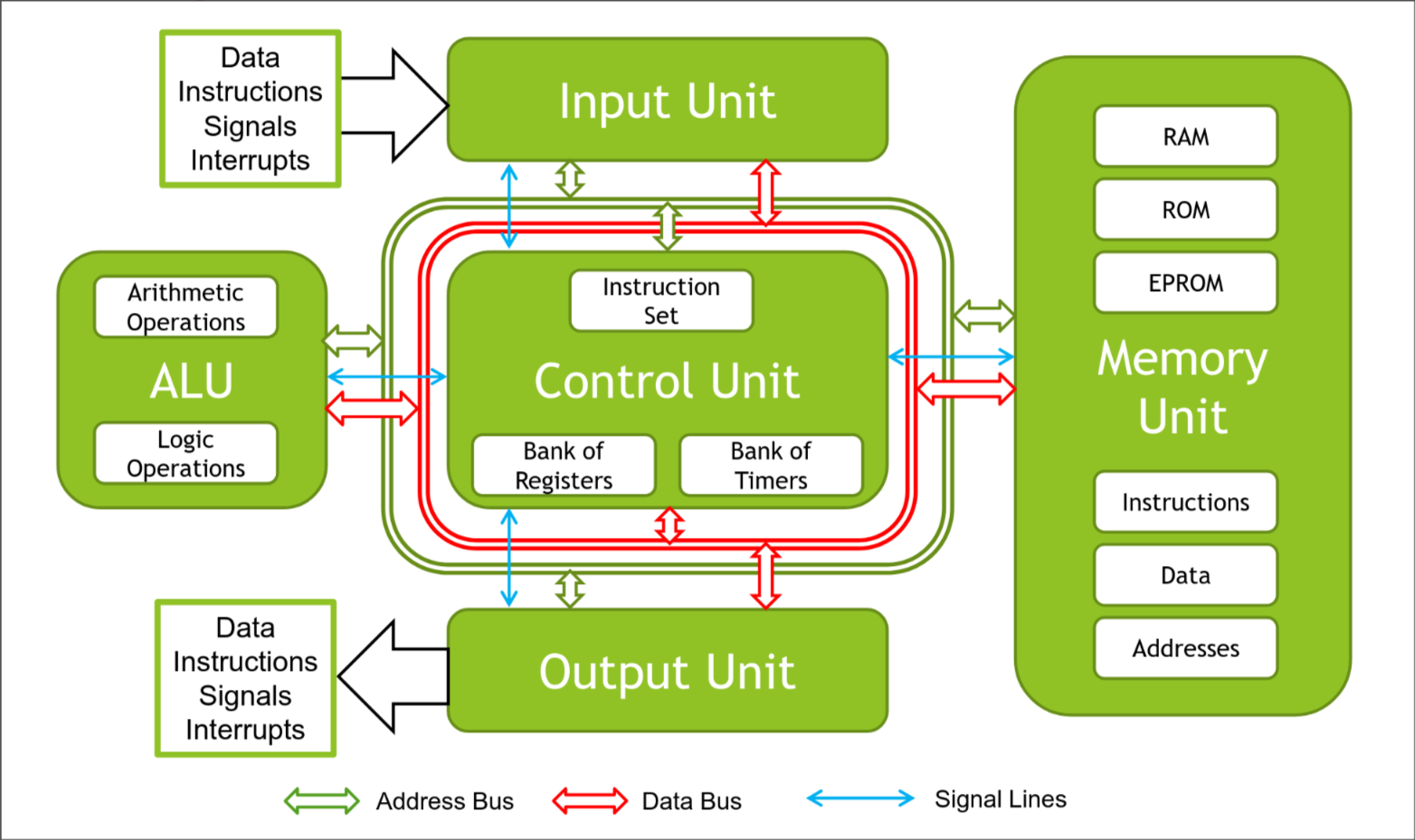
Van Neumann Architecture
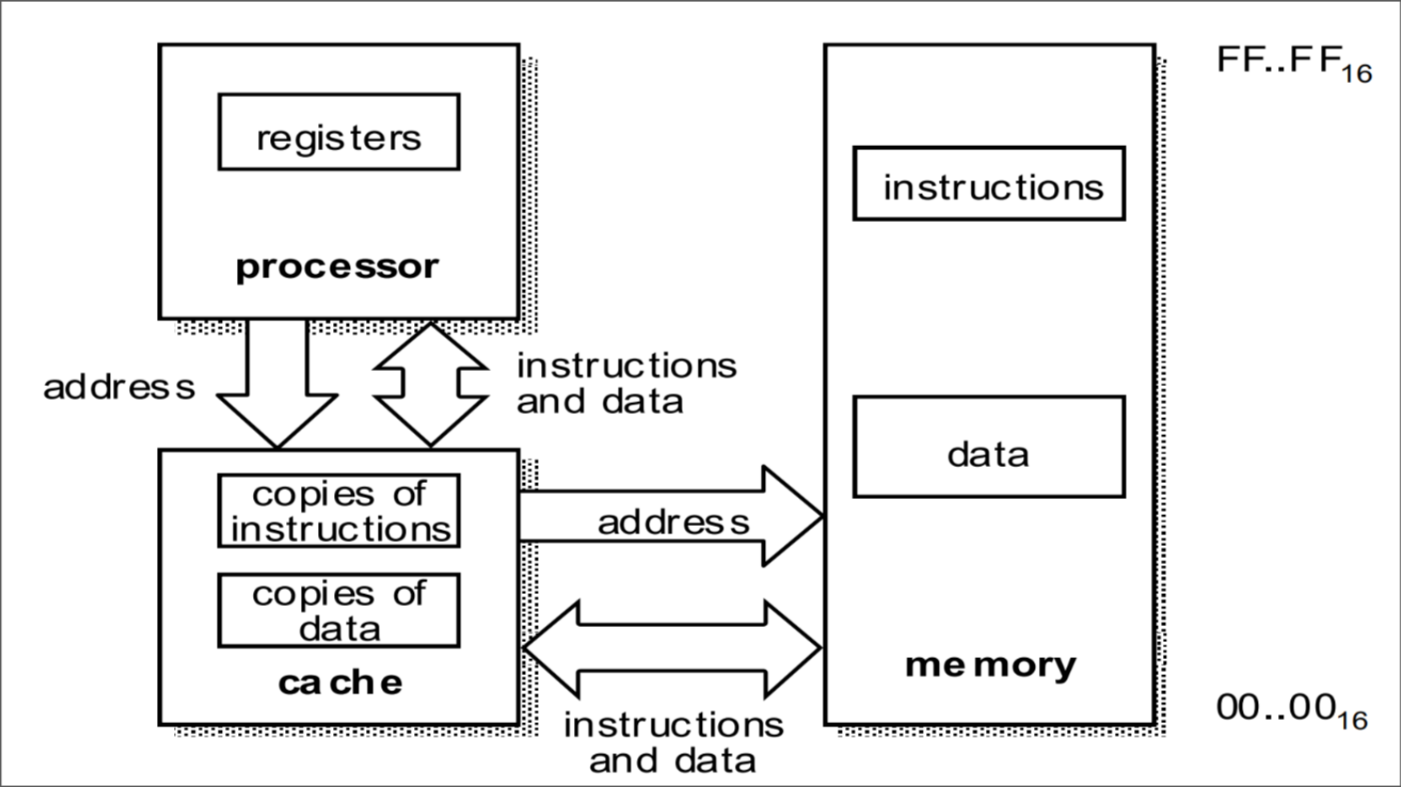
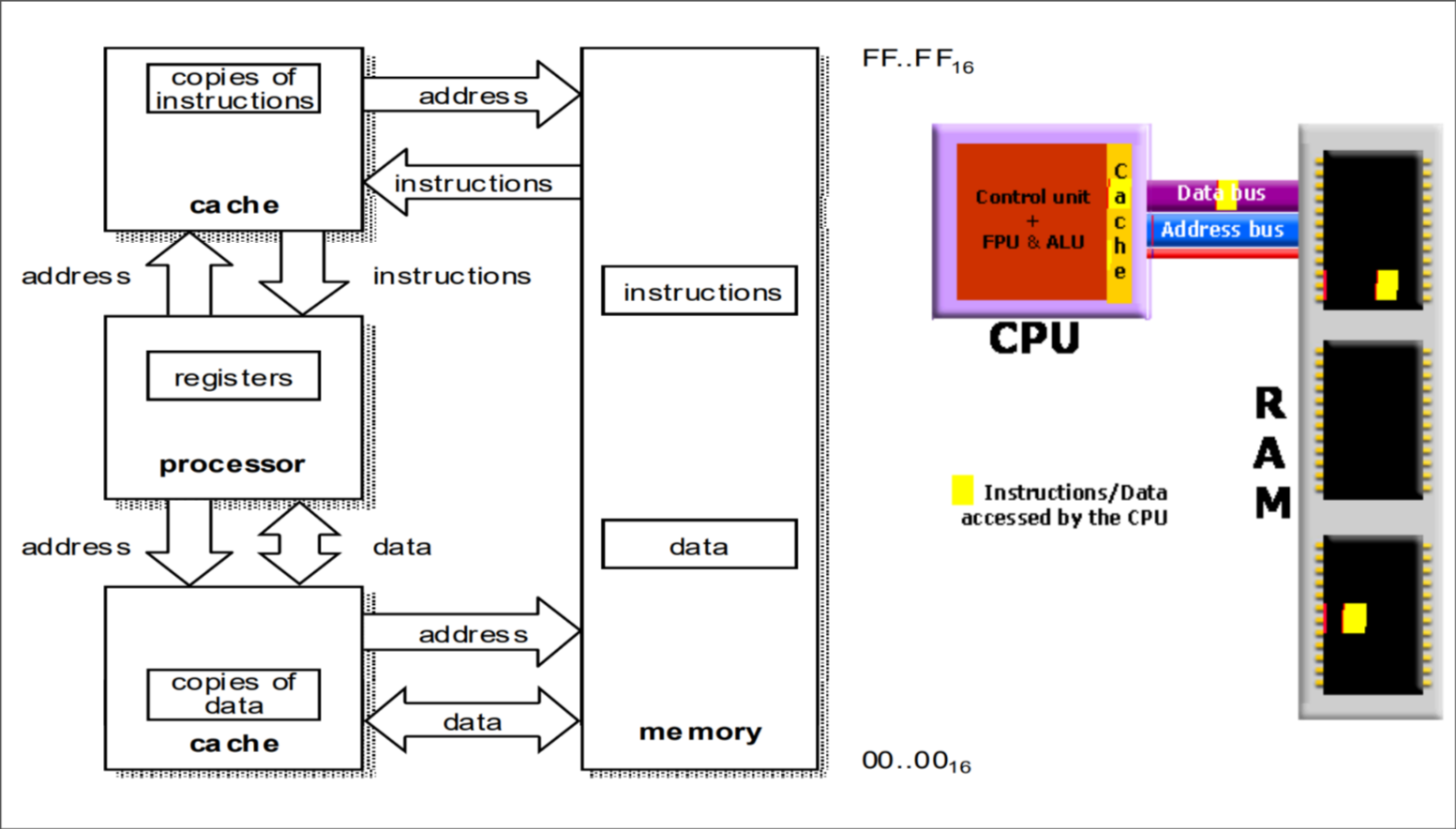
Harvard Architecture
Inventors of Digital Computer
Father of computers - Charles Babbage
- 1791-1871 George Boole 1815-1864 John von Neumann 1903-1957
Family of ARM Processors
ARM: Advanced RISC Machine
Cortex-M Series
For microcontrollers - e.g. street lamps
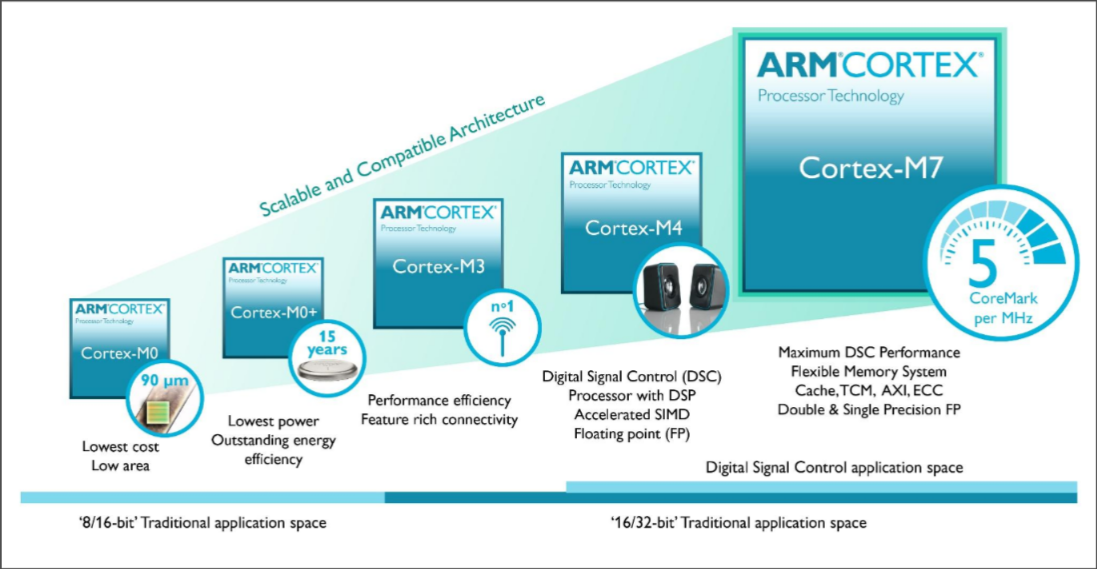
Cortex-R Series
For real-time applications - e.g routers
Cortex-A Series
For advanced application - e.g laptops
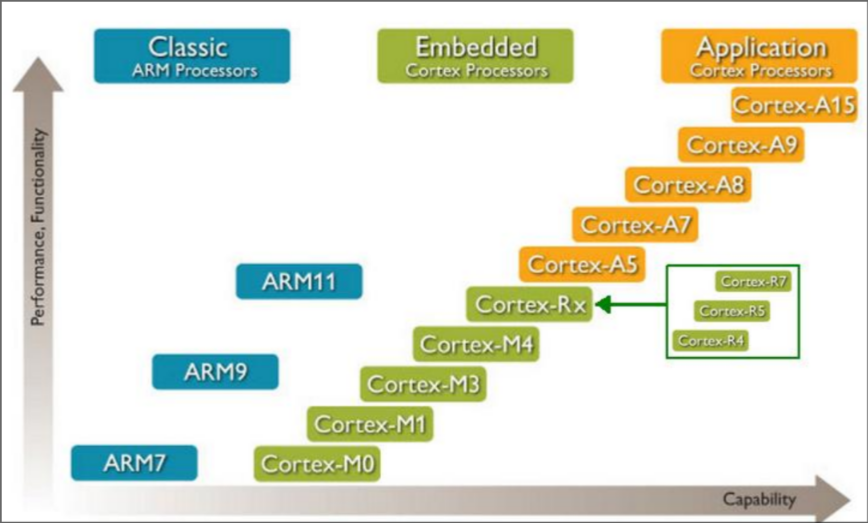
About ARM cortex
ARM is a RISC architecture
- ISA stands for Instruction Set Architecture which are innate
- RISC stands for Reduced Instruction Set Computer
- Most instructions execute in a single cycle
- ARM Instruction Set is 32-bit
- Thumb Instruction Set is 16/32-bit
ARM Cortex is a 32-bit load store architecture
- 8 bit - byte
- 16 bit - 2 byte - halfword
- 32 bit - 4 byte - word
- 64 bit - 8 byte - double-word
- The only memory accesses are loads and stores
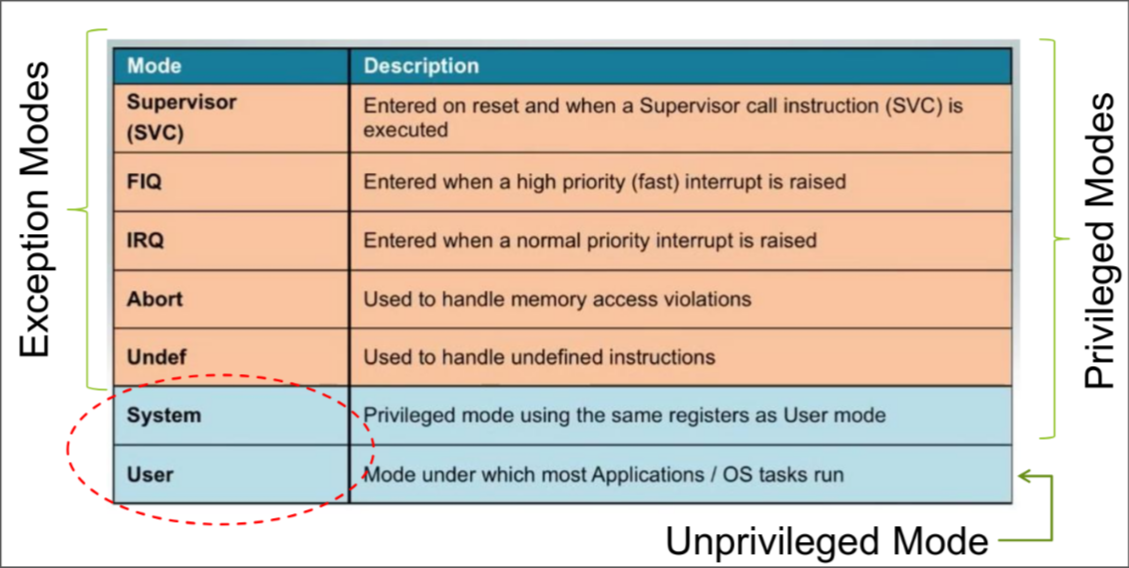
ARM Cortex supports system & user mode
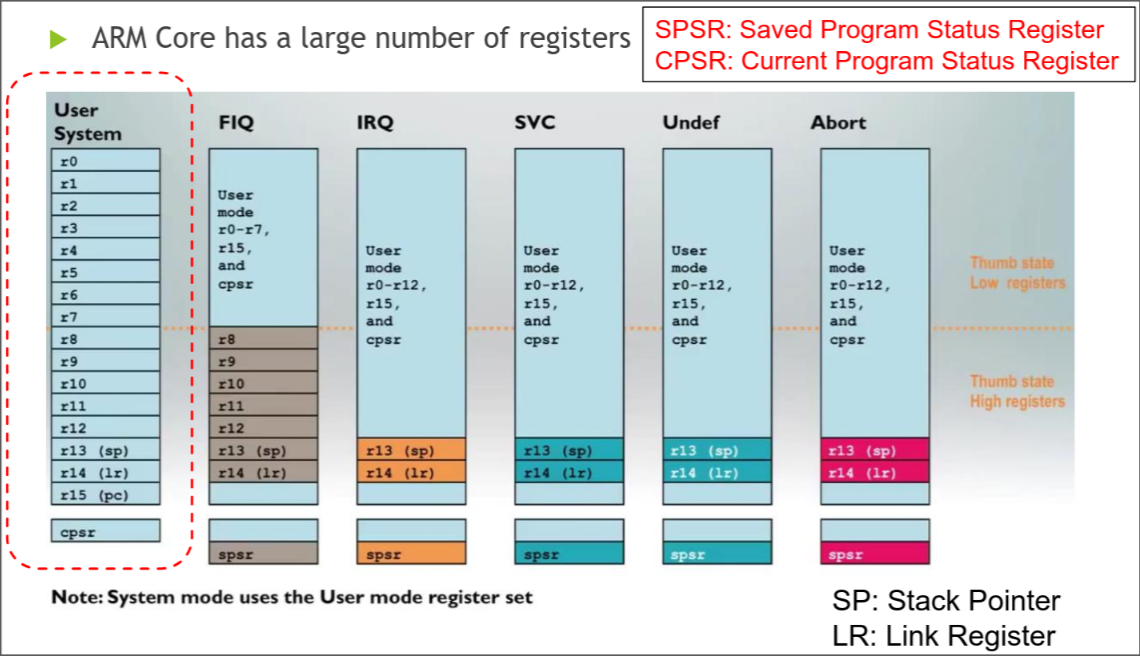
ARM Cortex has over 16 registers
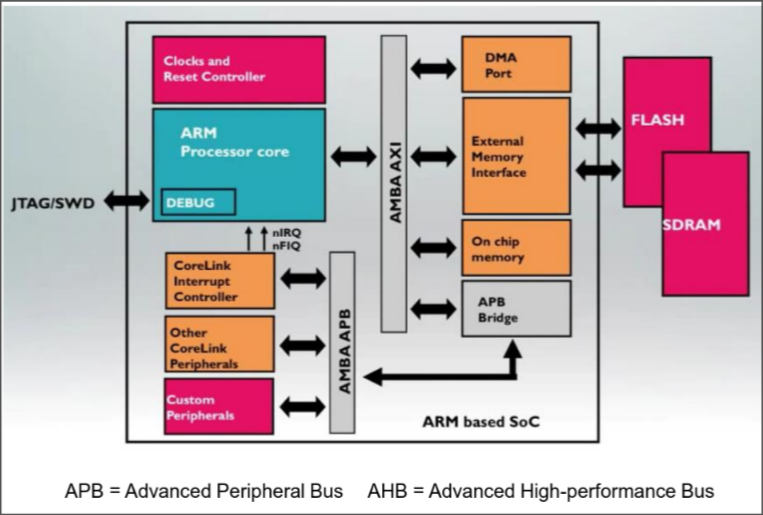
ARM has two internal buses
The ARM Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture (AMBA) is an open-standard, on-chip interconnect specification for the connection and management of functional blocks in system-on-a-chip (SoC) designs. It facilitates development of multi-processor designs with large numbers of controllers and peripherals.
ARM Cortex supports Fast Interrupt request (FIQ)
An FIQ is just a higher priority interrupt request, that is prioritized by disabling IRQ and other FIQ handlers during request servicing. Therefore, no other interrupts can occur during the processing of the active FIQ interrupt.
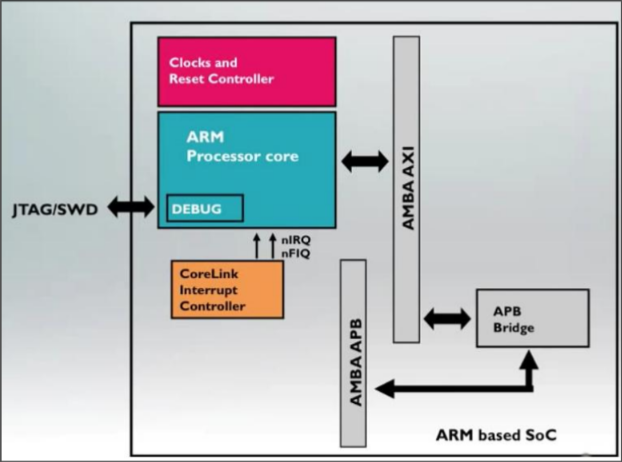
ARM Cortex supports Direct Memory Access (DMA)
Direct memory access (DMA) is a feature of microprocessor systems that allows certain hardware subsystems to access main system memory such as RAM (Random Access Memory) independently of the central processing unit (CPU).
ARM Cortex includes debug port → IDE
JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) specifies the use of a dedicated debug port implementing a serial communications interface for low-overhead access without requiring direct external access to the system address and data buses.
Return to MA4832 Microprocessor Systems - Home