Orthographic Projection
Drawing Standards
Line types:
-
Visual Aid
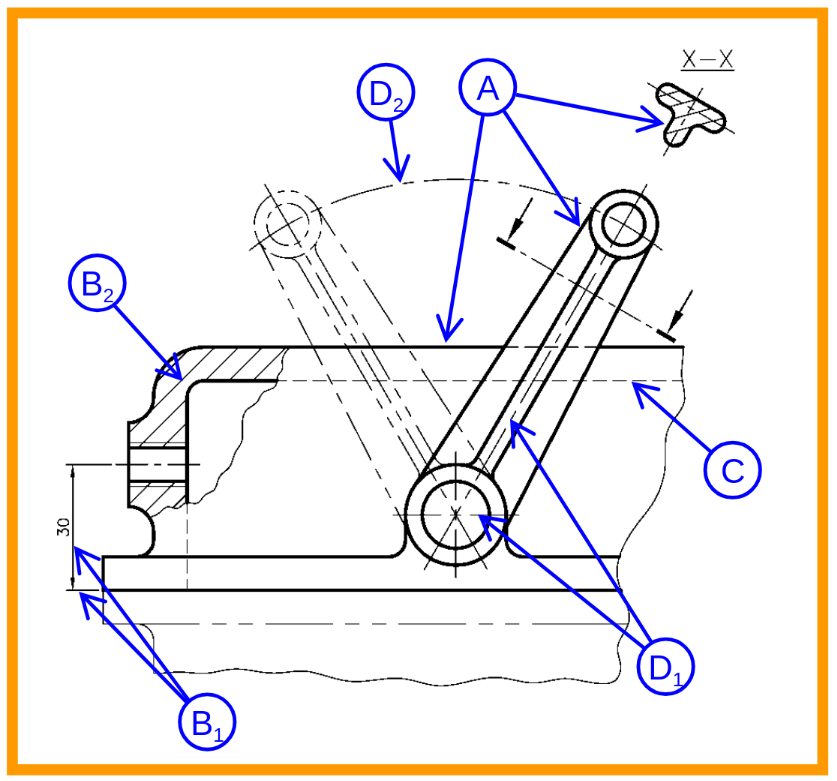
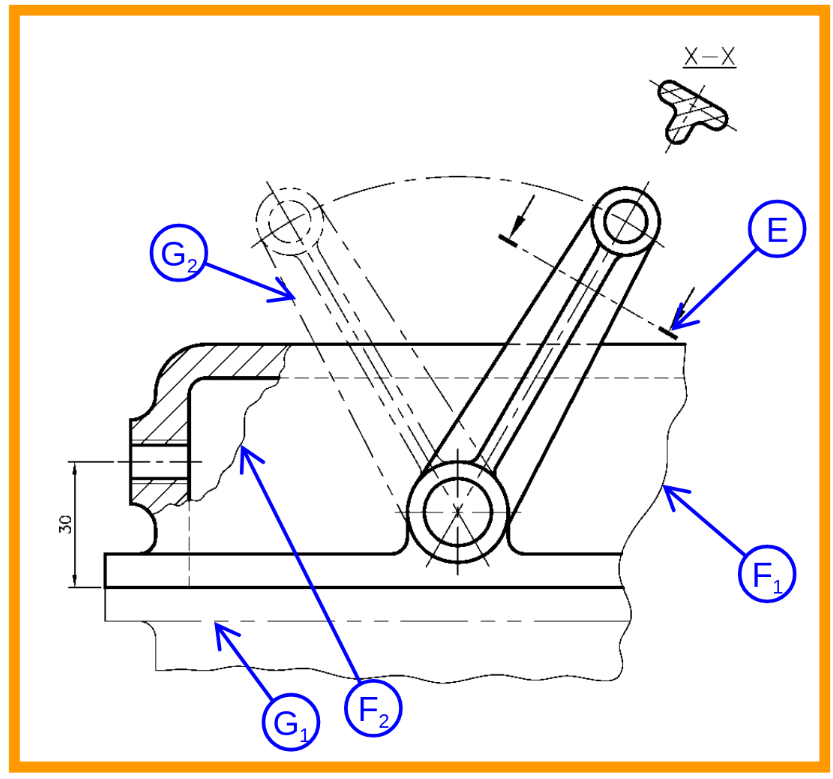
| A | Thick Continuous | Visible outlines & Edges |
| B | Thin Continuous | Dimension, Projection line, Hatching line |
| C | Thin Short dashes | Hidden outlines & Edges |
| D | Thin Chain | Centre lines, Pitch lines |
| E | Thin Chain, Thick Ended | Cutting plane |
| F | Thin continuous Irregular | Limits of partial view / sections |
| G | Thin chain short double dashes | Outlines of adjacent parts. Alternative and extreme positions of movable parts. Initial outlines prior to forming. |
Precedence of Line
Visible line > Hidden line > Center line
-
Hidden line - Thin short dashes
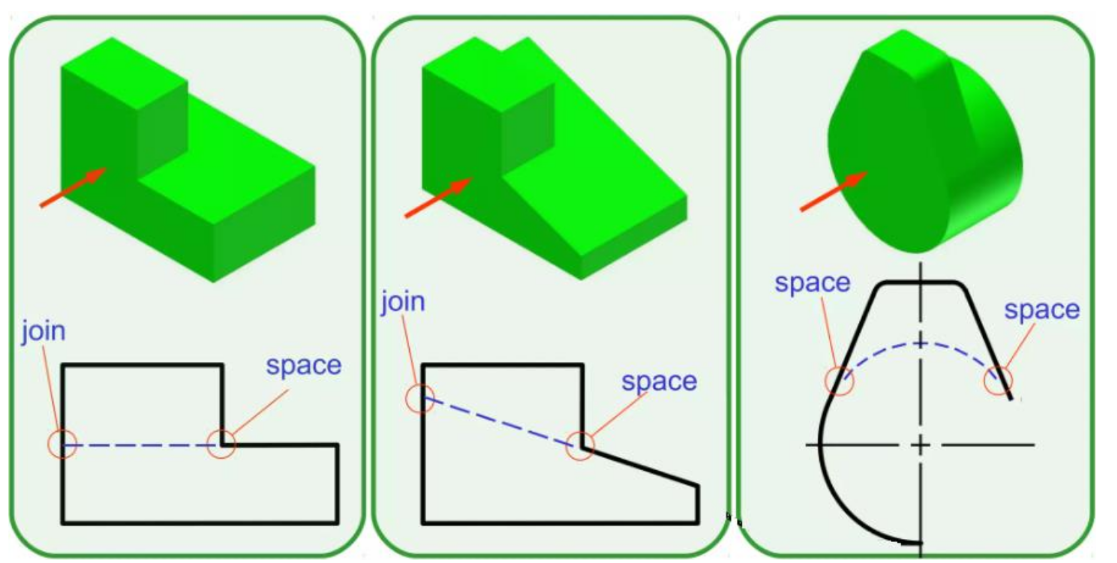
Intersections of hidden lines should form L, T, V or Y corners
-
Centre lines - for symmetrical axis, bolt circles and path of motion
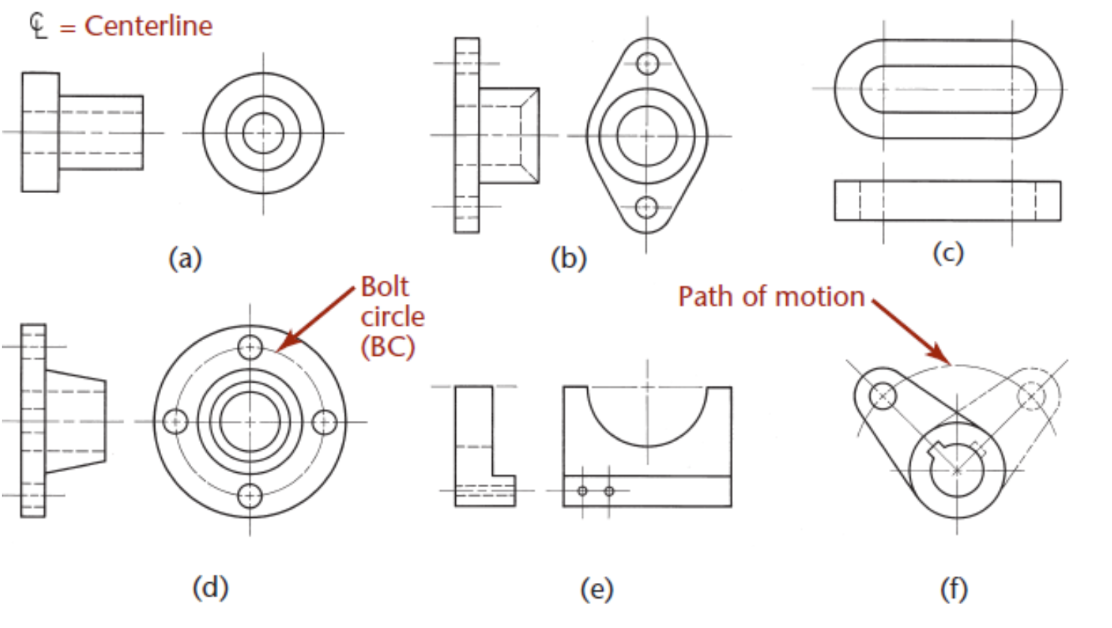
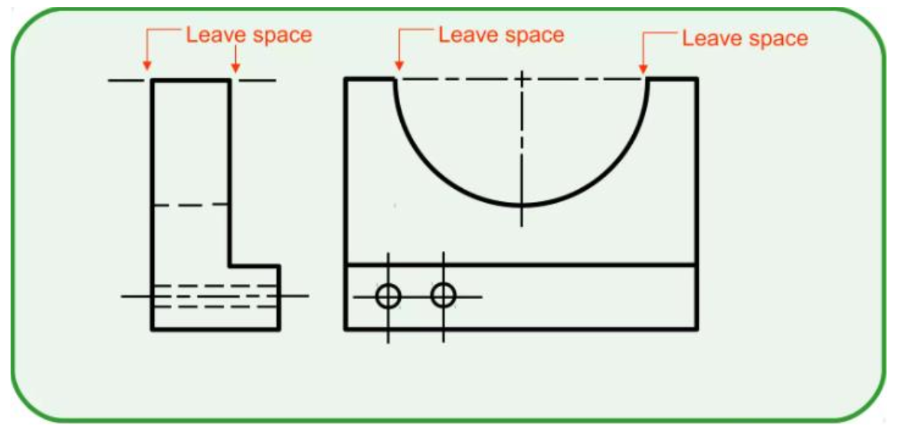
can be thin continuous line for small hole
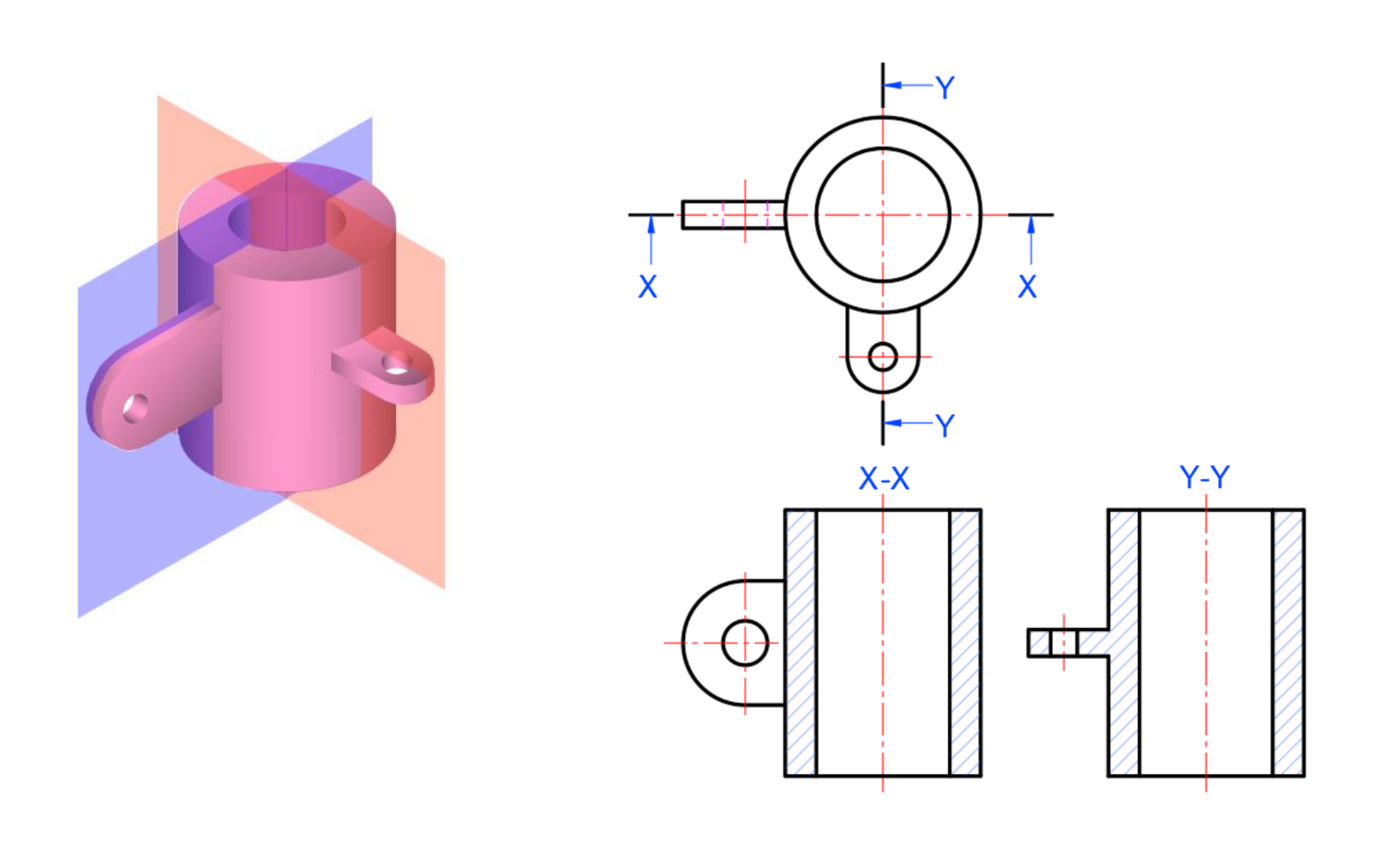
Orthographic Systems
-
First angle Projection
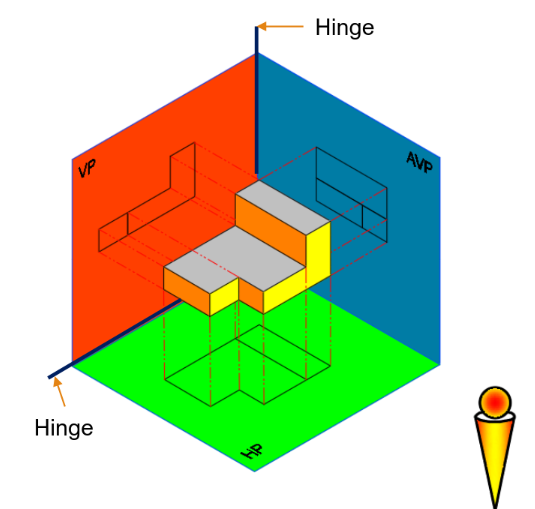
-
Third angle Projection
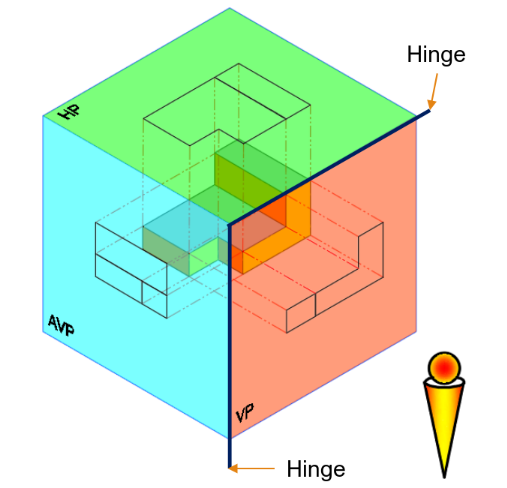
-
ISO Projection Symbols
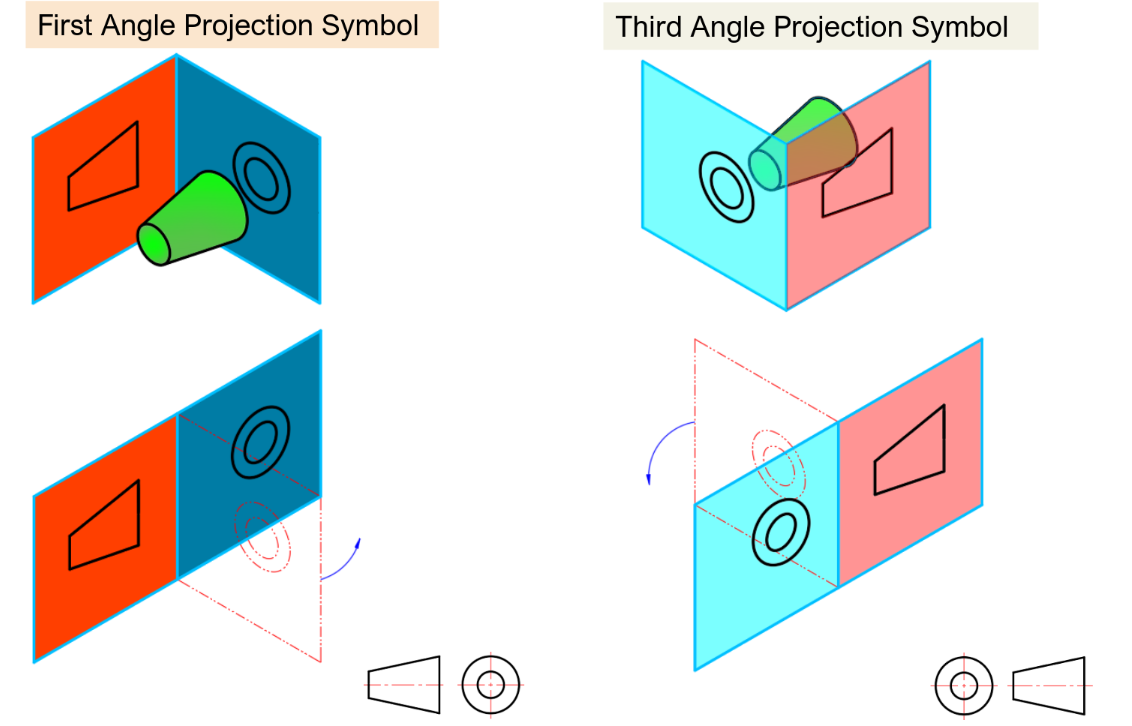
First angle is projected past the sight-line while third angle is projected back towards the sight-line
Isometric Drawing
Isometric — all angles are equal (30to horizontal) True-length distances are shown along isometric lines Hidden lines should be omitted unless absolutely necessary to completely describe the object
Visualising Orthographic Views
A straight, visible or hidden line means:
- Edge between two surfaces
- Edge view of a surface
- Limiting element of a curved surface
Normal surface
Parallel to plane of projection
-
True shape is projected onto that plane
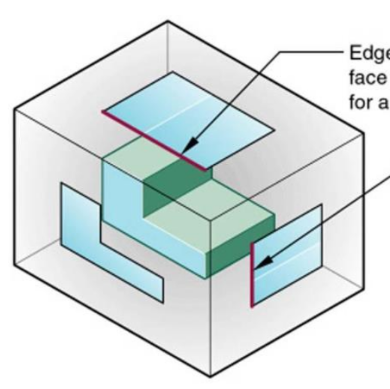
Inclined surface
Perpendicular to one plane of projection but inclined to adjacent planes
-
Edge view - True length on perpendicular plane
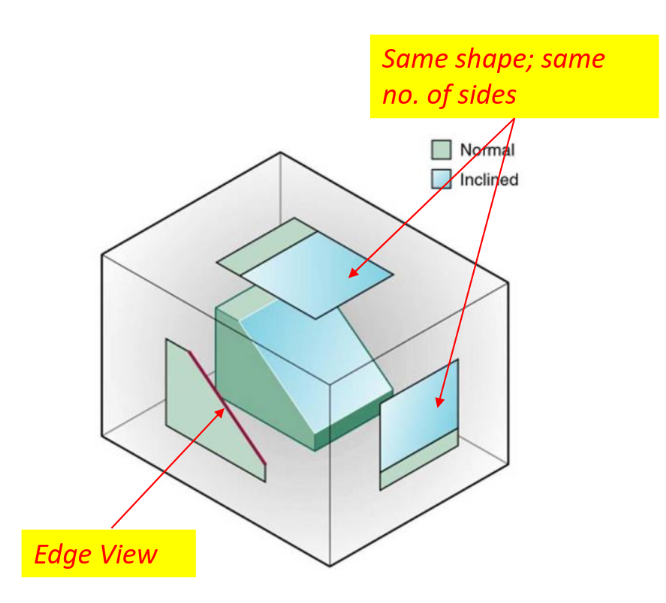
-
Same shape; same no. of sides on adjacent planes
Oblique surface
Inclined to all principle planes
-
does not appear true size in any standard view
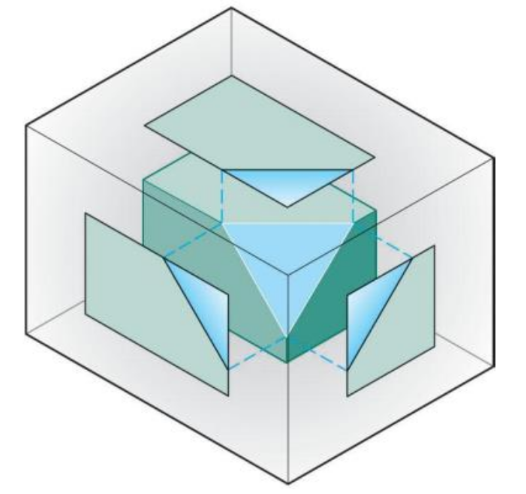
-
Parallel edges on the object appear parallel on all views
Holes & Threads
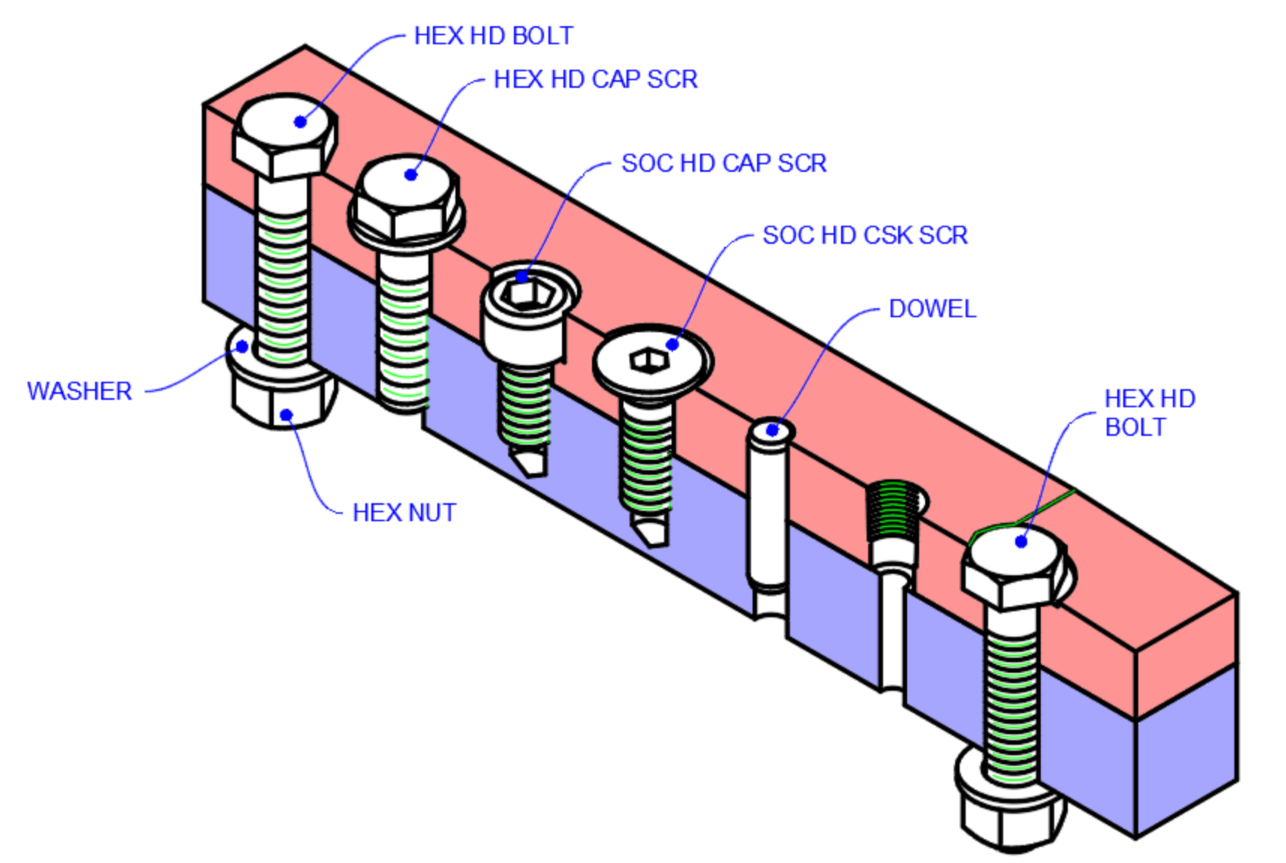
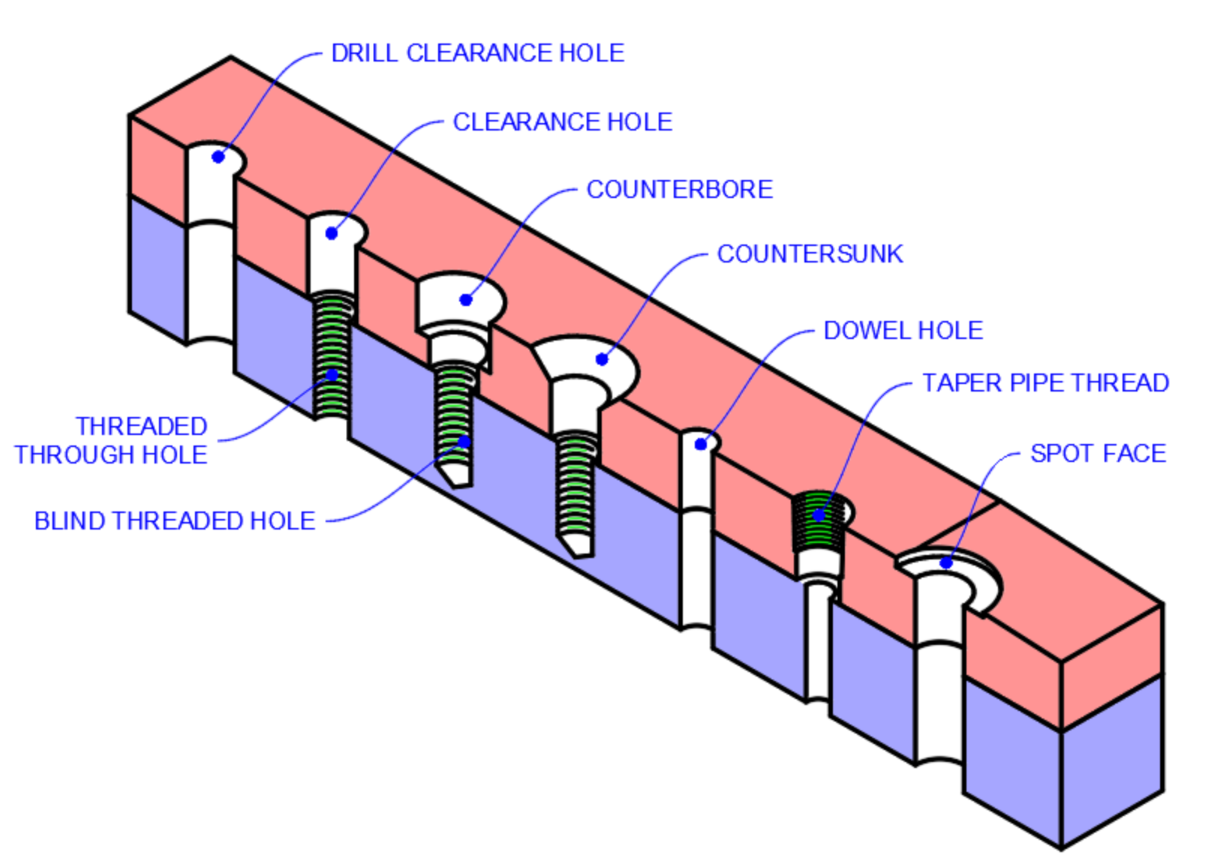
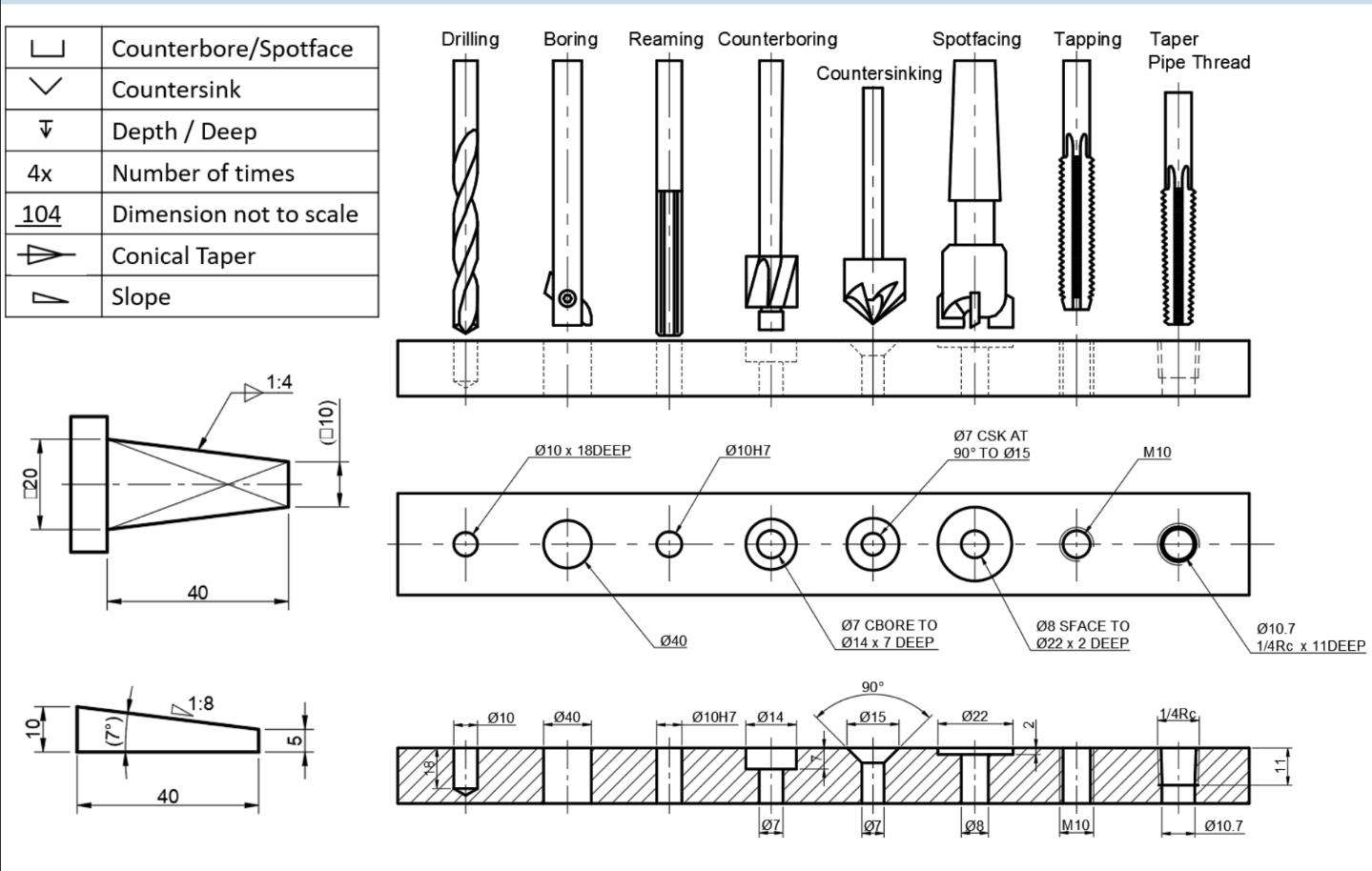
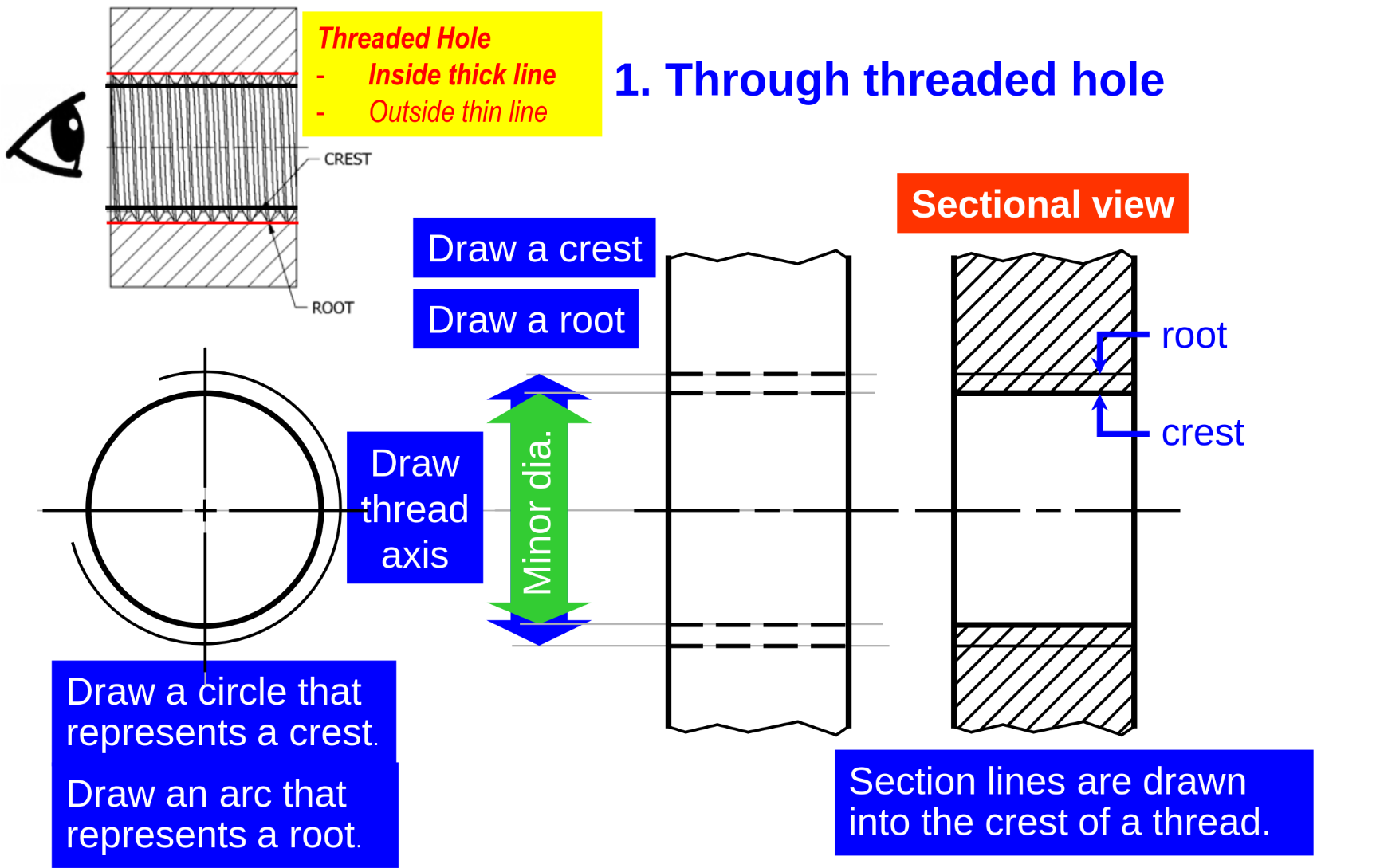
-
Threaded hole drawing
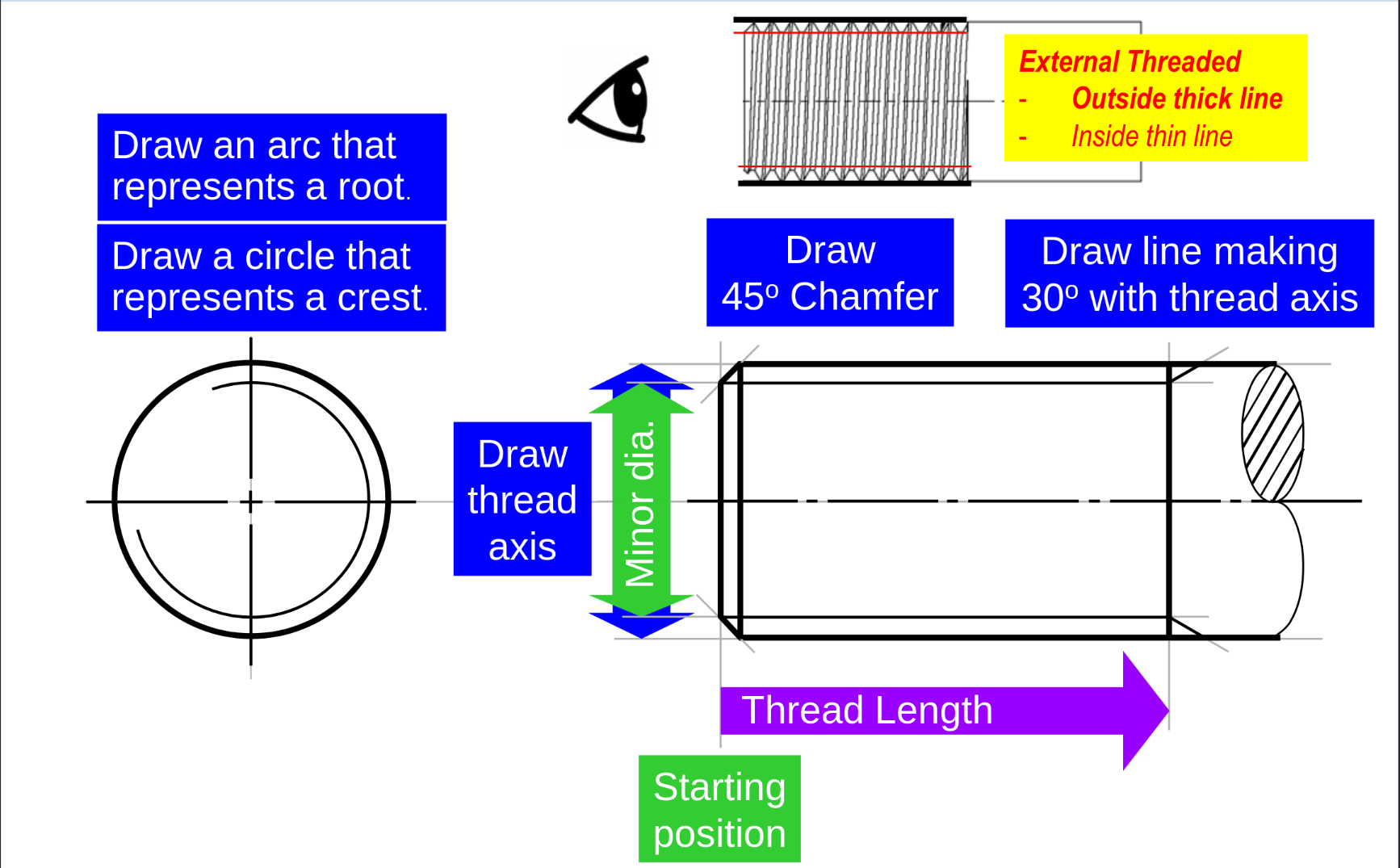
-
External thread drawing
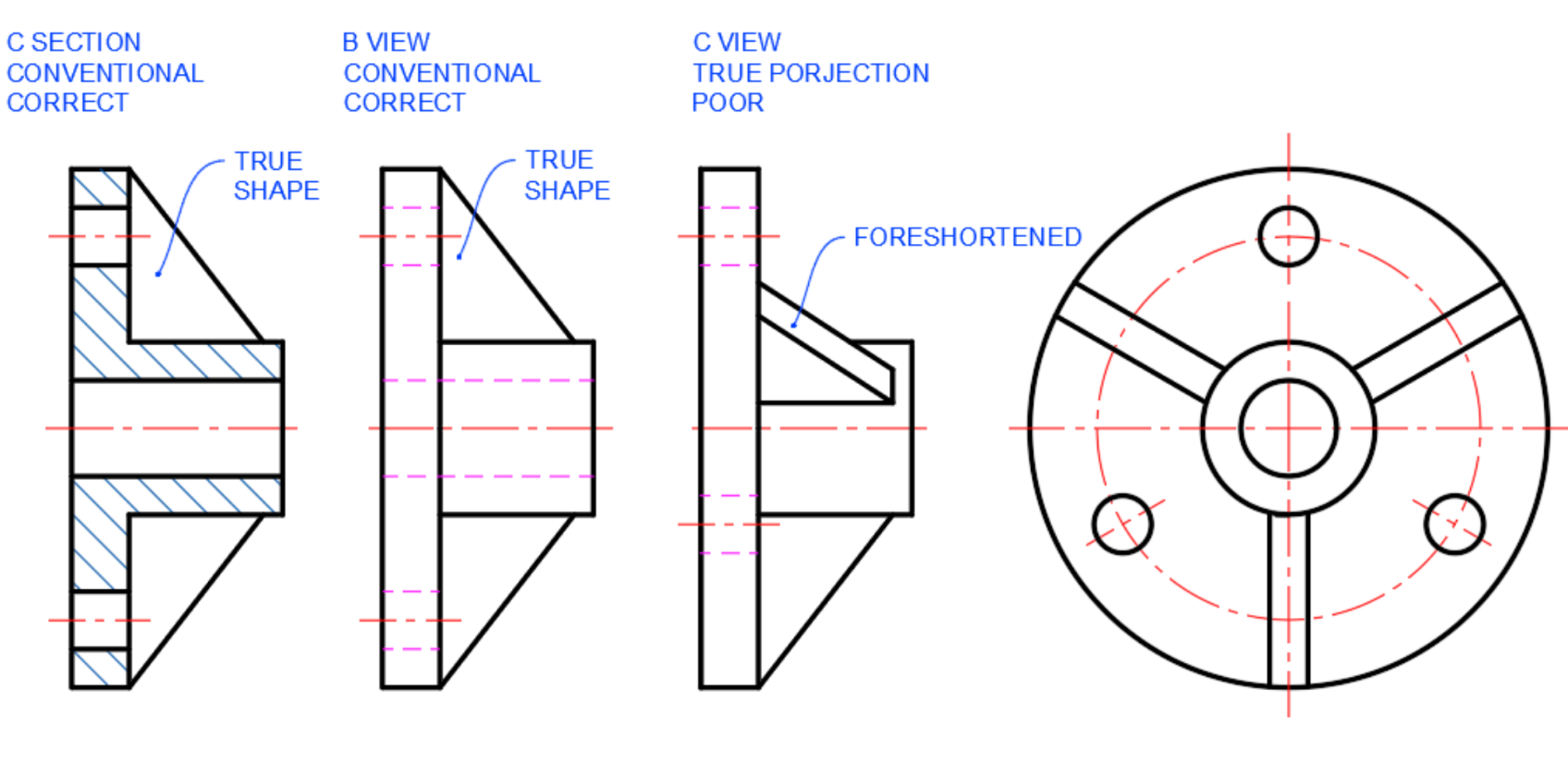
Sectioning
To show internal features clearly, minimising hidden lines
Full Sectioning
Features
-
Features shown — behind cutting plan
-
No hidden lines
-
No need to section parts with no interior details (e.g. Shaft, screws, bolts)
- Particularly ribs and lugs — unless transversely cut Hatching
-
Hatched area should be completely bounded by outline
-
Same part — hatch in same direction & spacing
-
Hatching should not be parallel to outline
-
Thin parts can be completely black — gaps between thin parts needed for clarity Special cases
-
Lugs
-
Ribs
-
Spoke
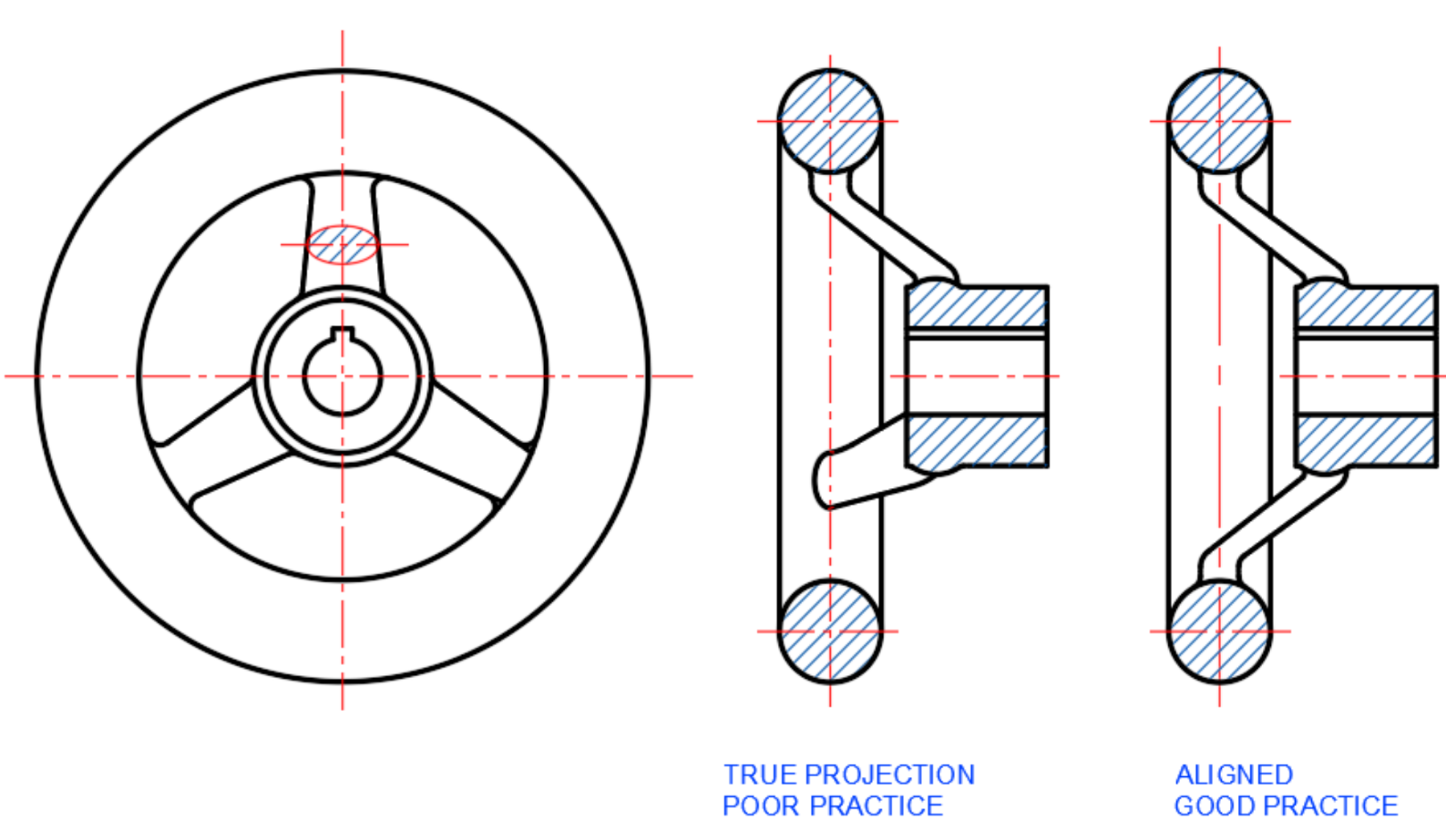
Offset Section
To show internal details that lie on more than 1 parallel plane
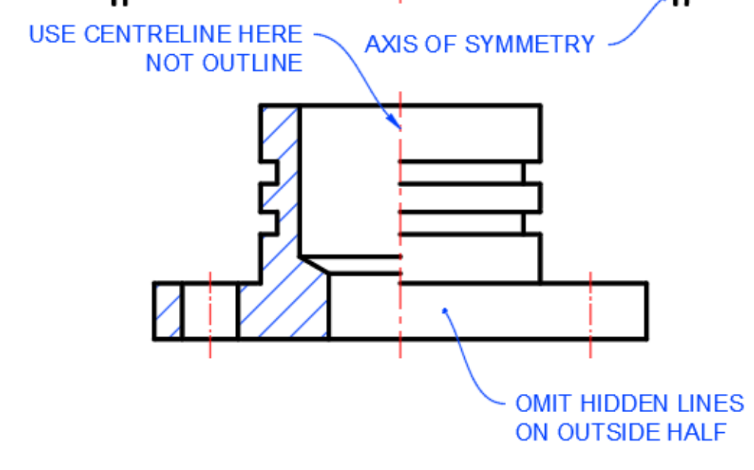
Half Section
-
Center line seperates sectioned half from unsectioned half
-
Hidden line is omitted in unsectioned half
Aligned section
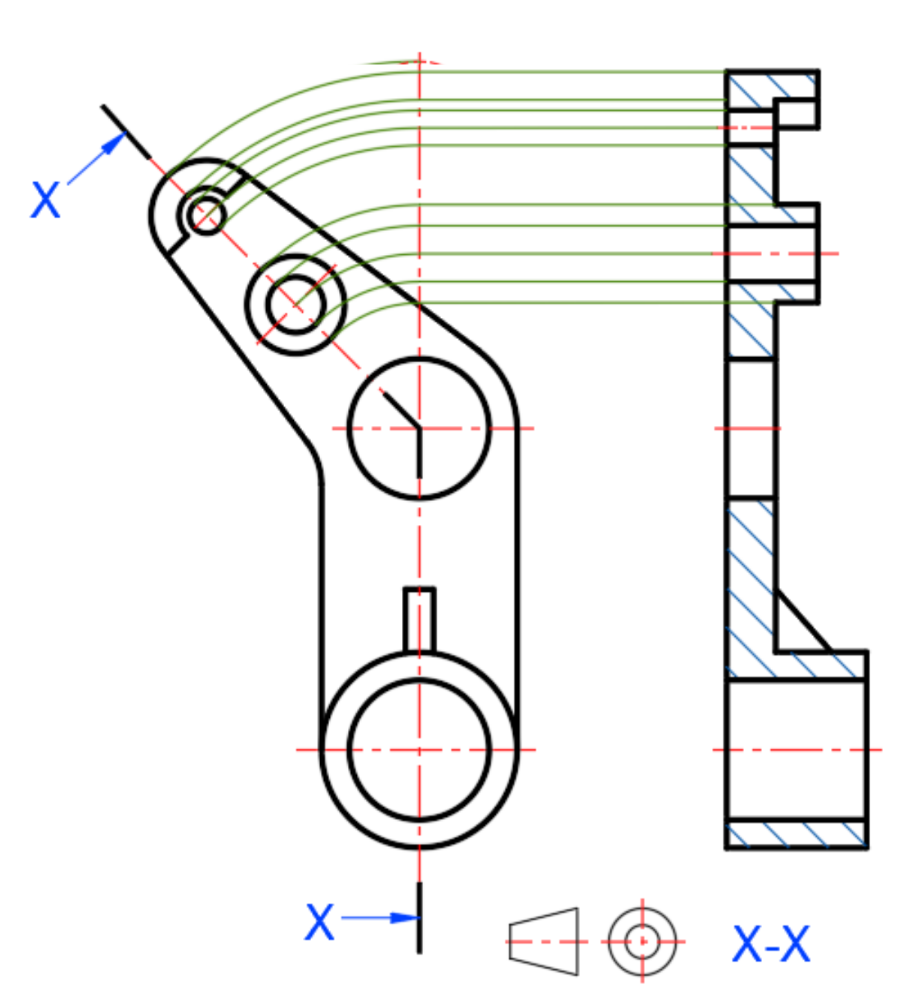
Revolved section
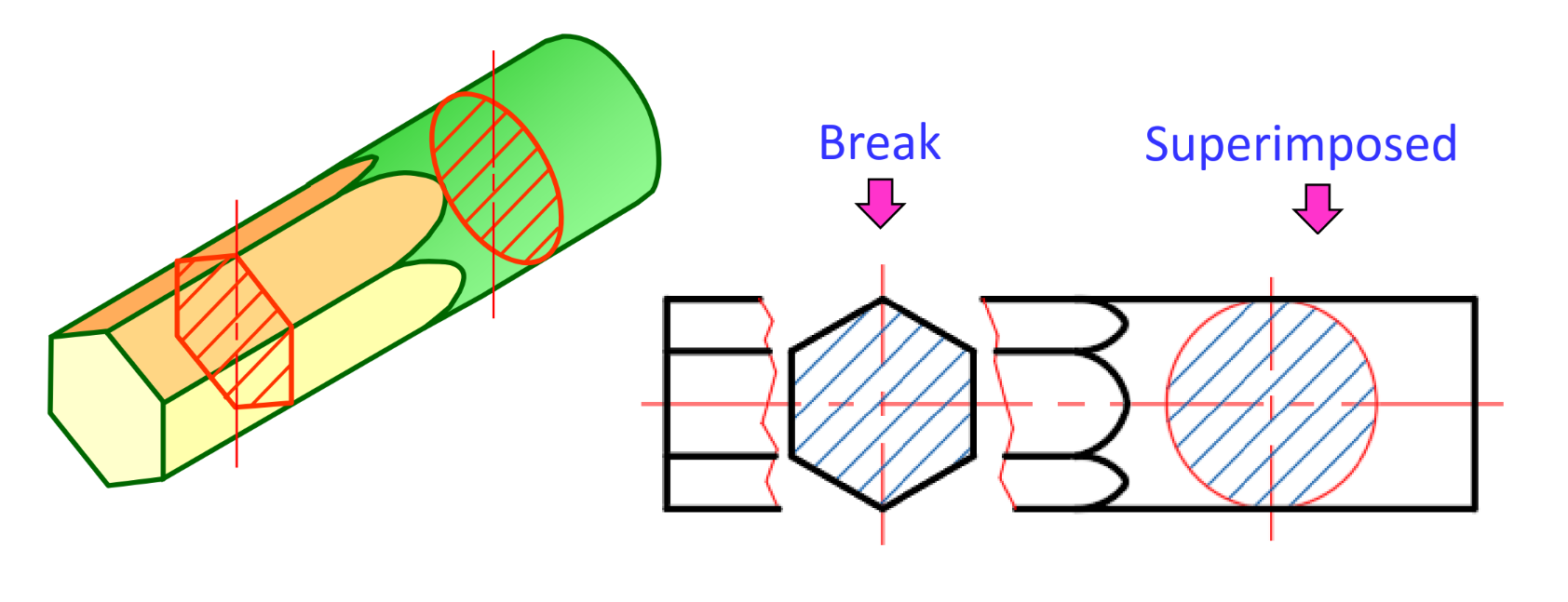
True length
By Aux view
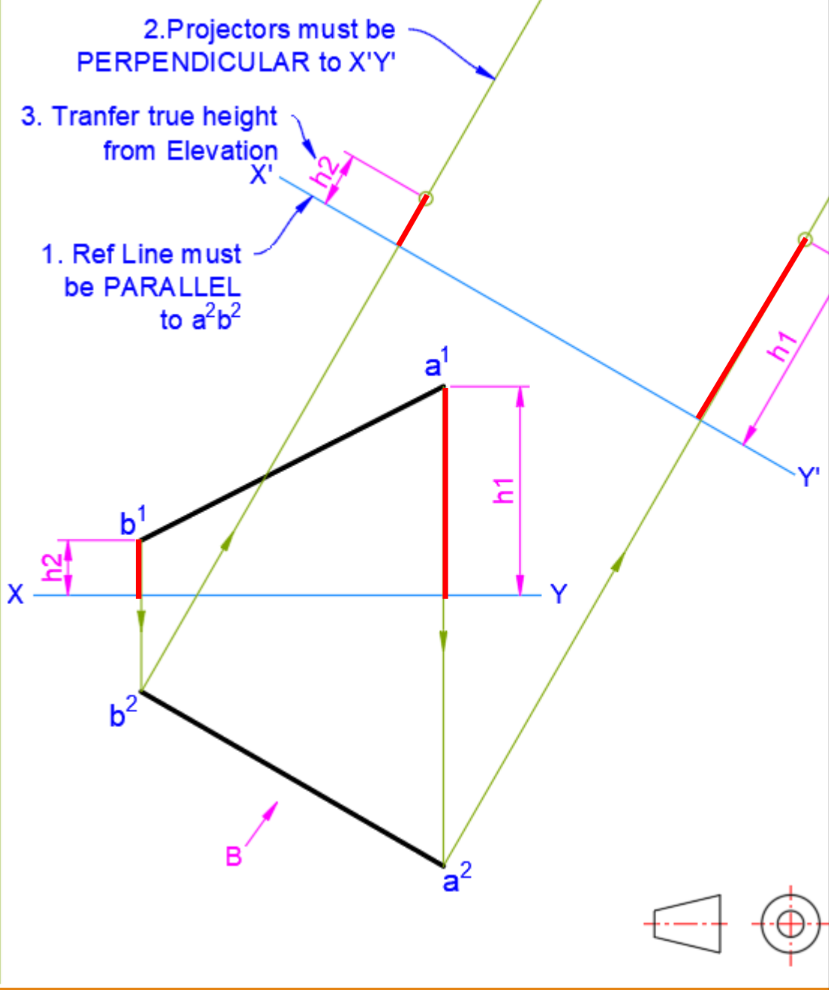
Identifying TL
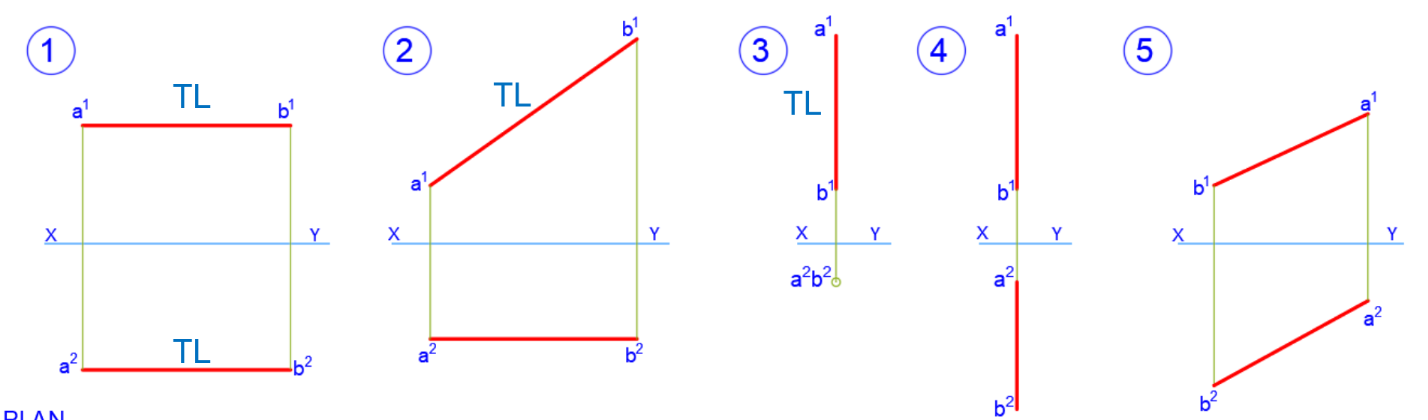
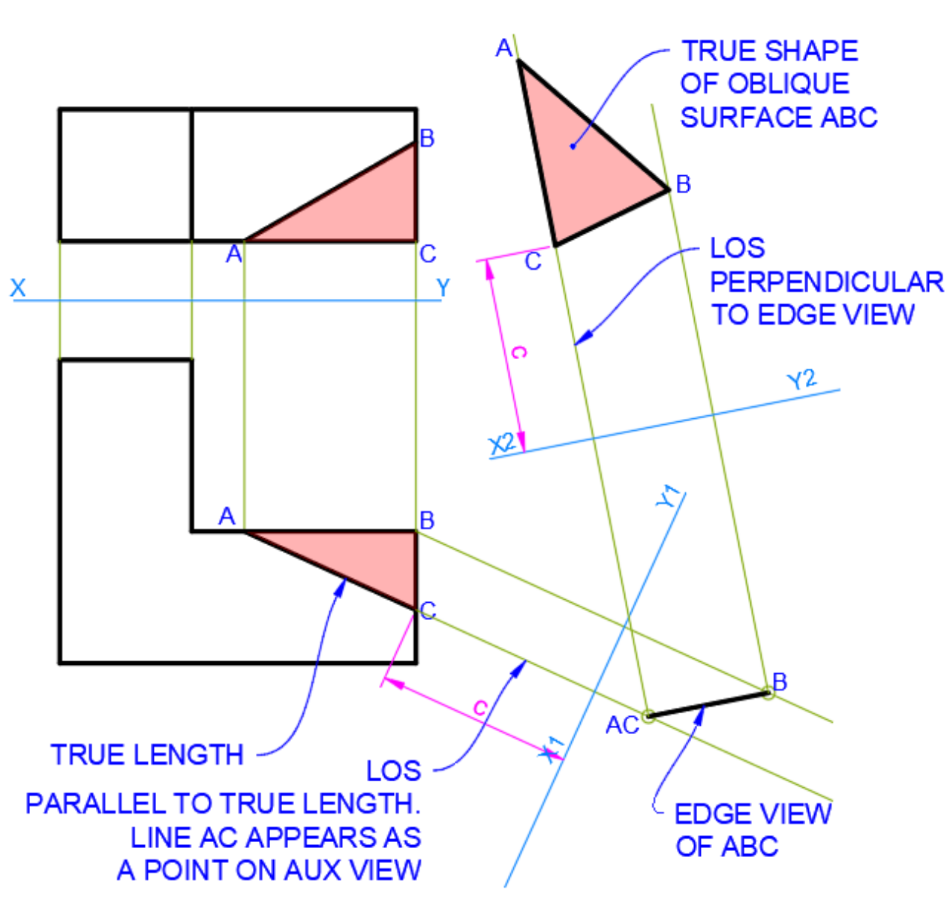
Finding True Shape
- Identify line with True Length
- Aux view perpendicularly to that line to find edge view (where plane is seen as a line)
- Aux view parallel to edge view to find true shape
Others
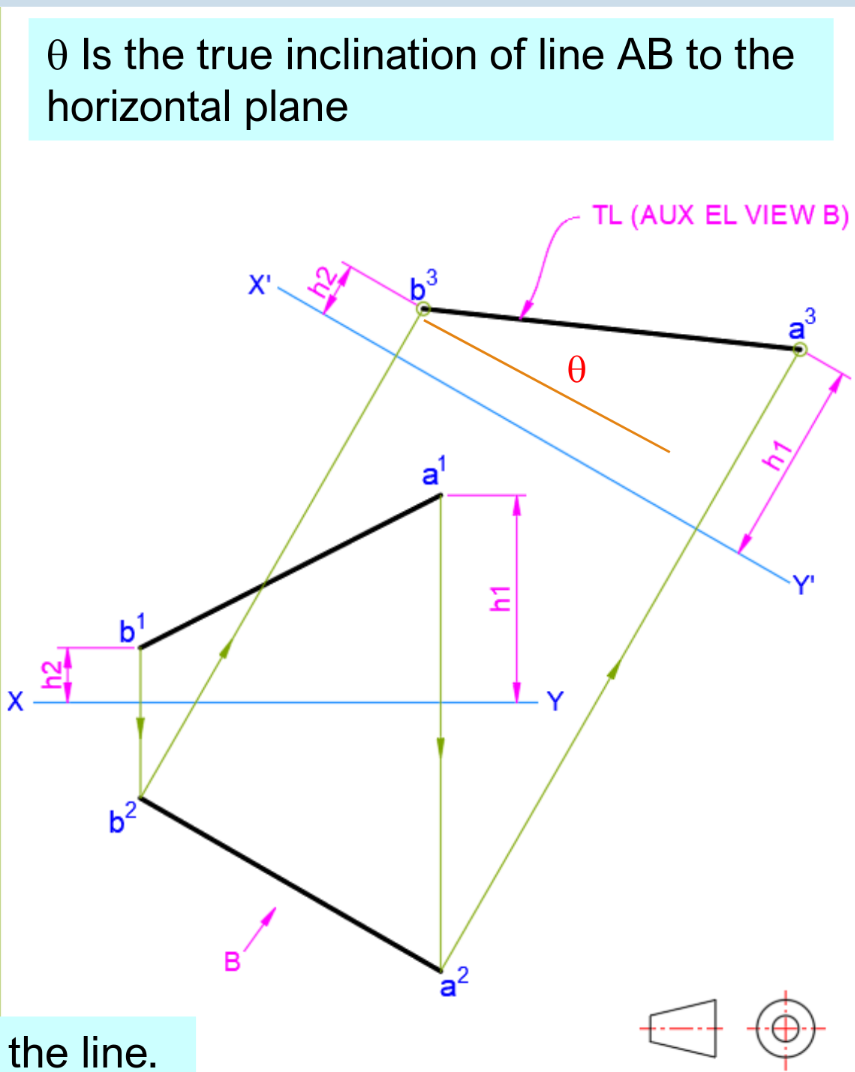
Dihedral Angle: Angle between two planes
- Angle between edge views Shortest distance
- Length between point(view) and line True angle
Auxiliary Projection
First vs Third angle
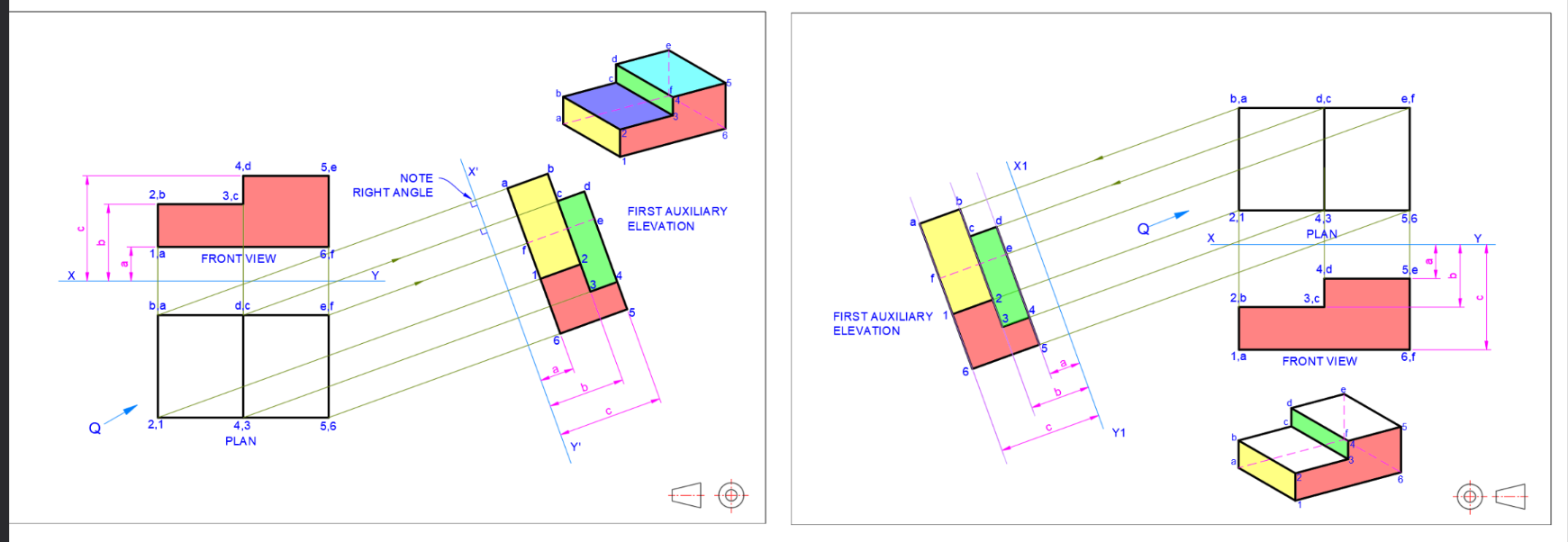 Views are the same, only relative position is changed
Views are the same, only relative position is changed
Dimensioning & Annotations
ISO R129 (Dimensioning) & ASME Y14.5 (GD&T)
Basic Information
Size & location of features — Material — Number required
Higher level Information
Tolerances (size and geometric) — Surface roughness — Assembly process description
Dimensioning practices
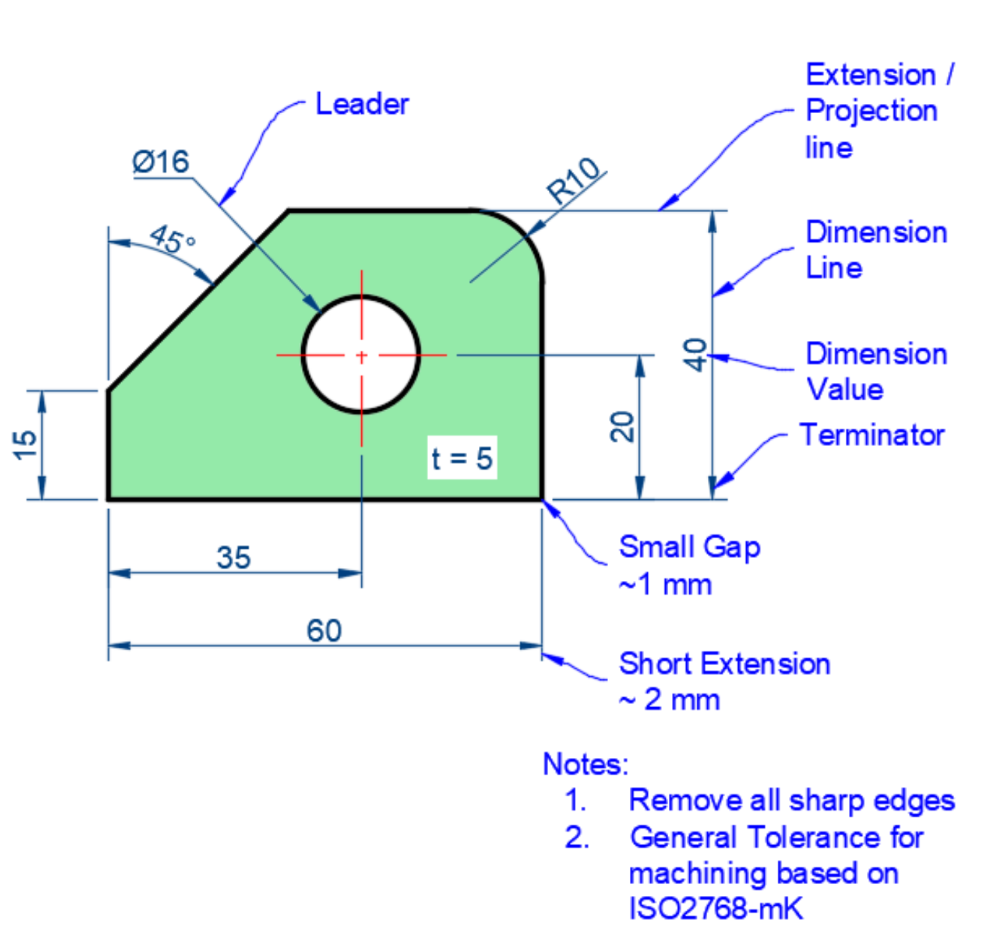
-
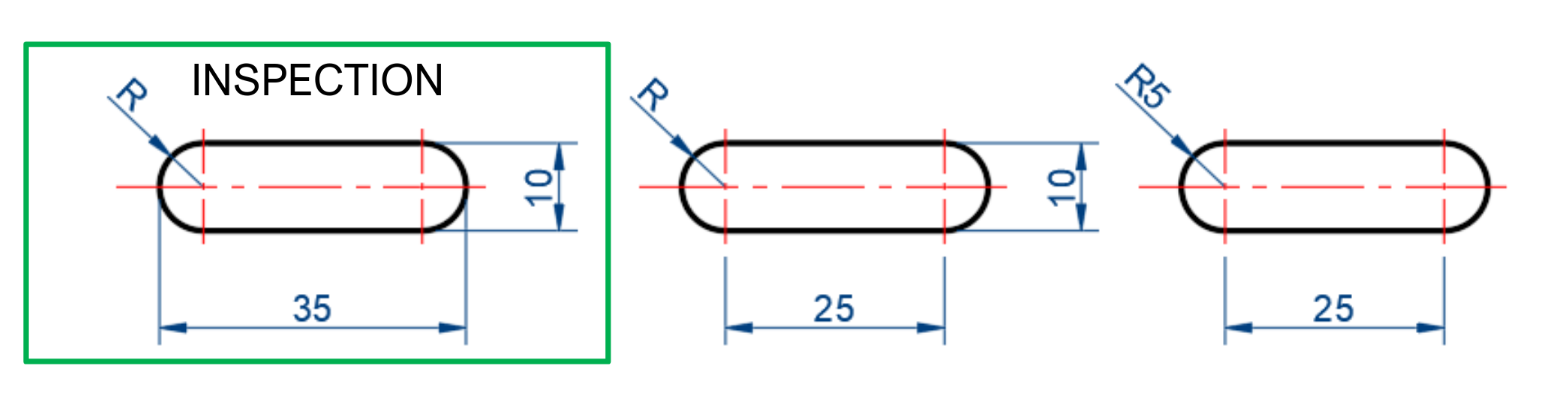
Radius
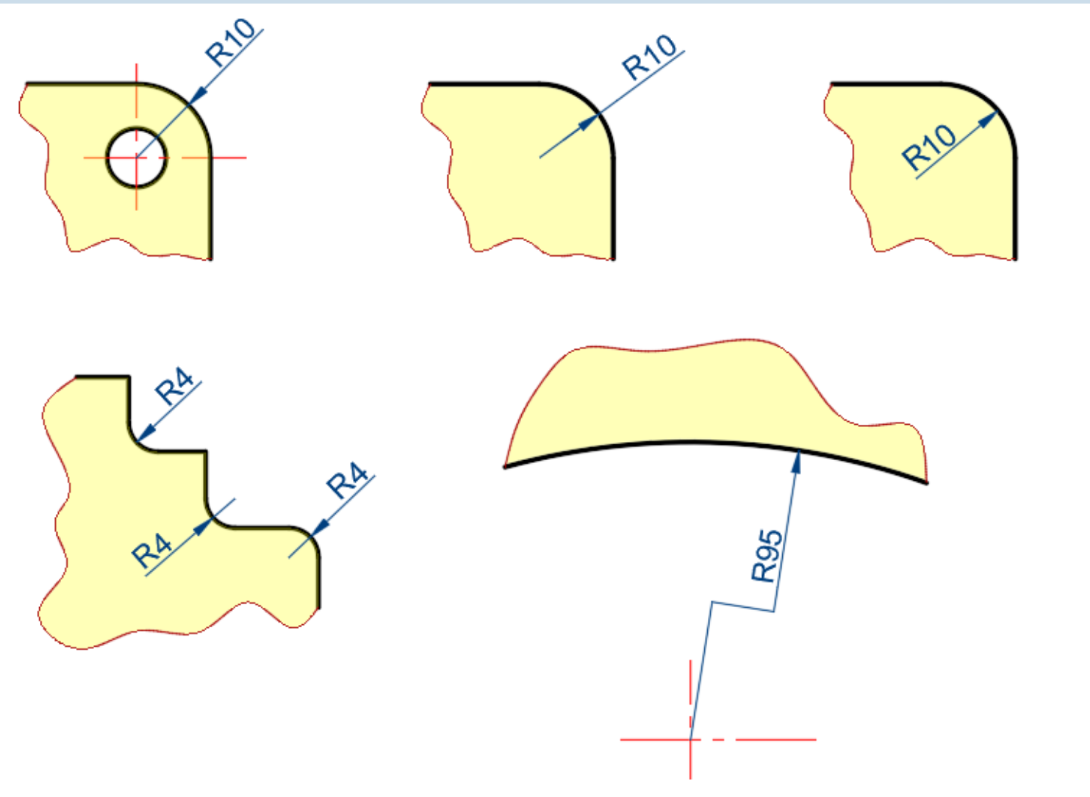
-
Spheric
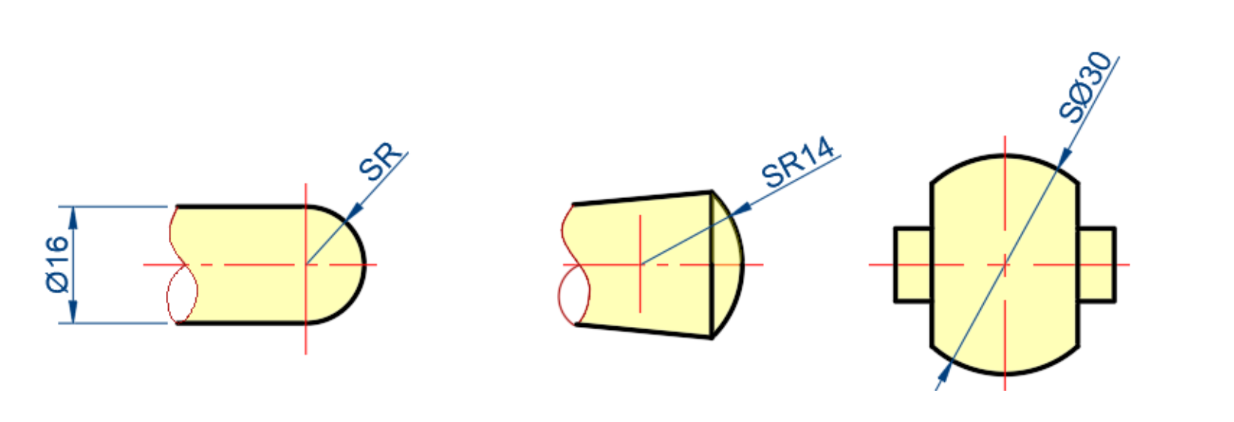
-
Chamfer
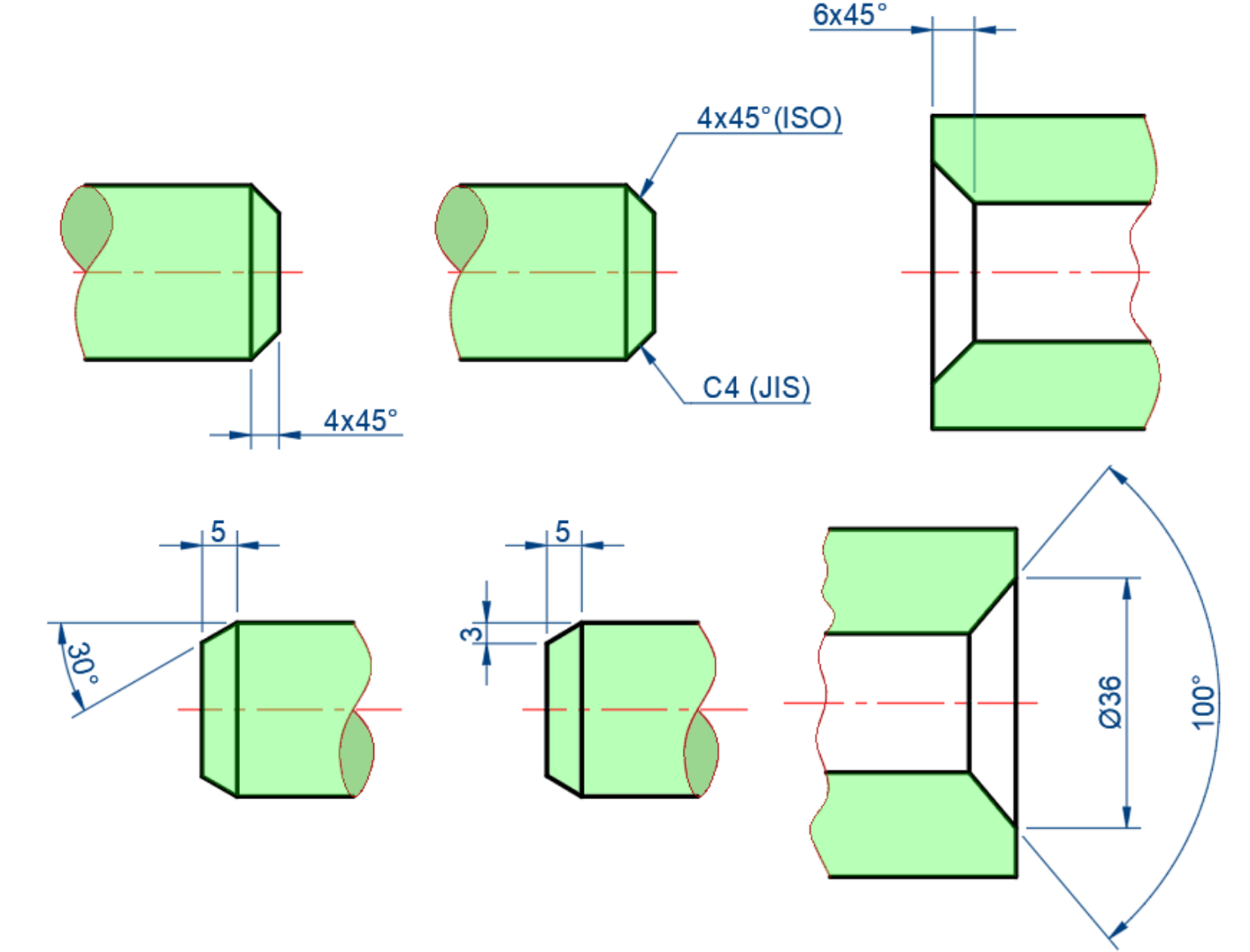
-
Taper / slope
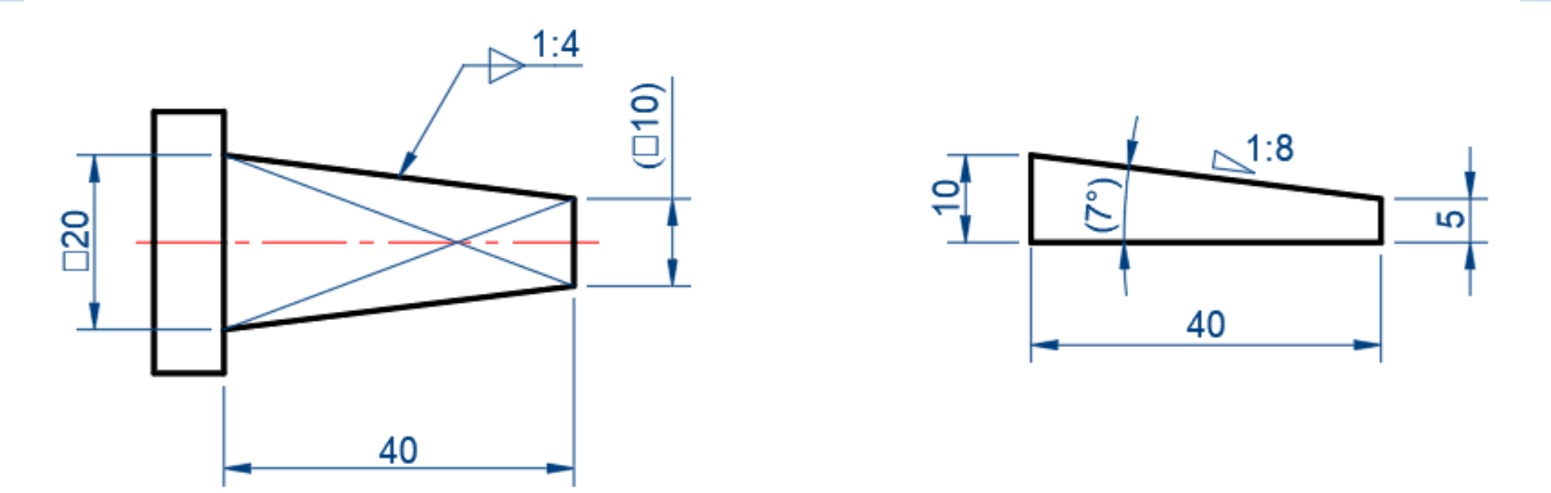
-
Keyway
-
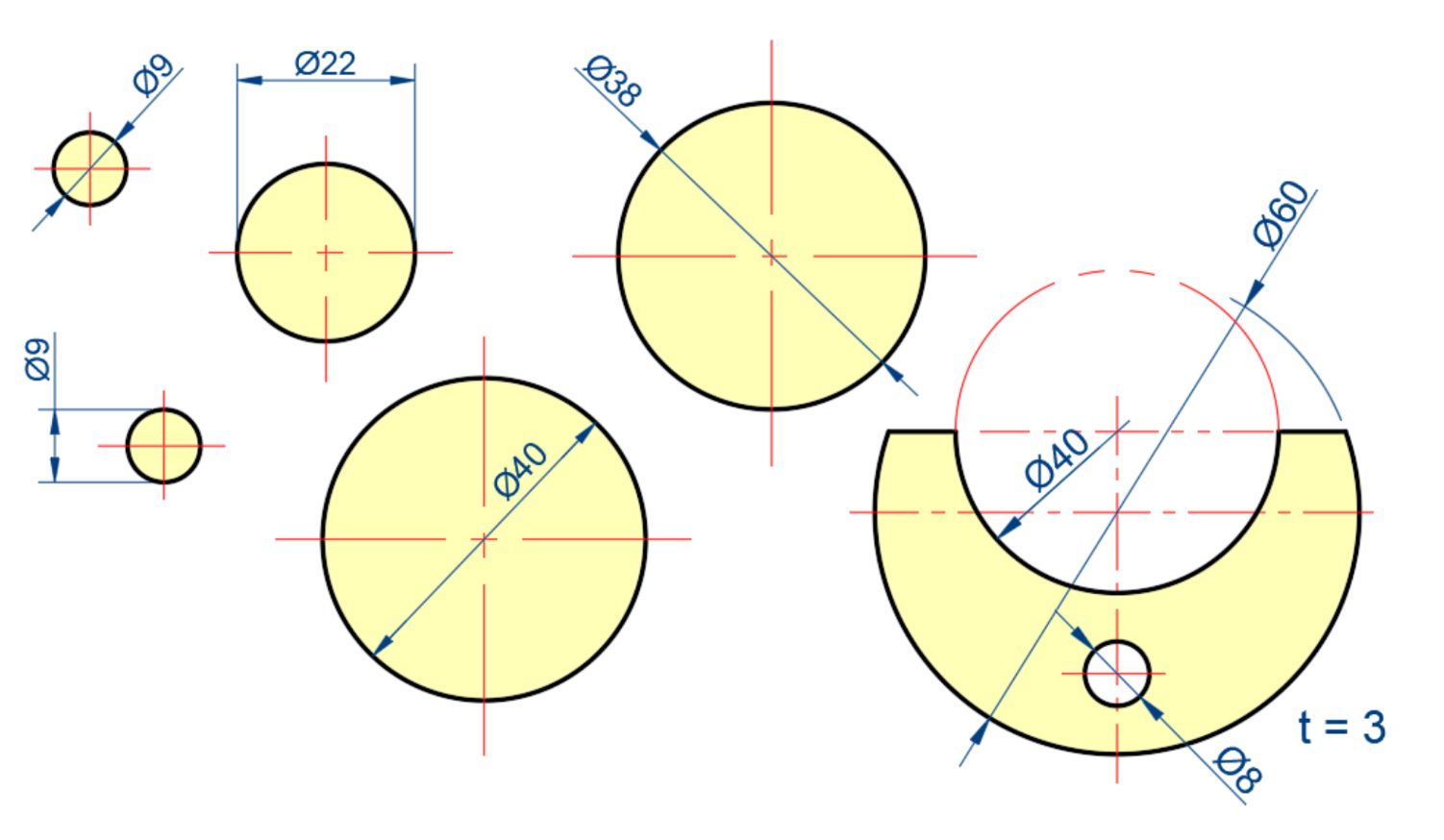
Diameter
-
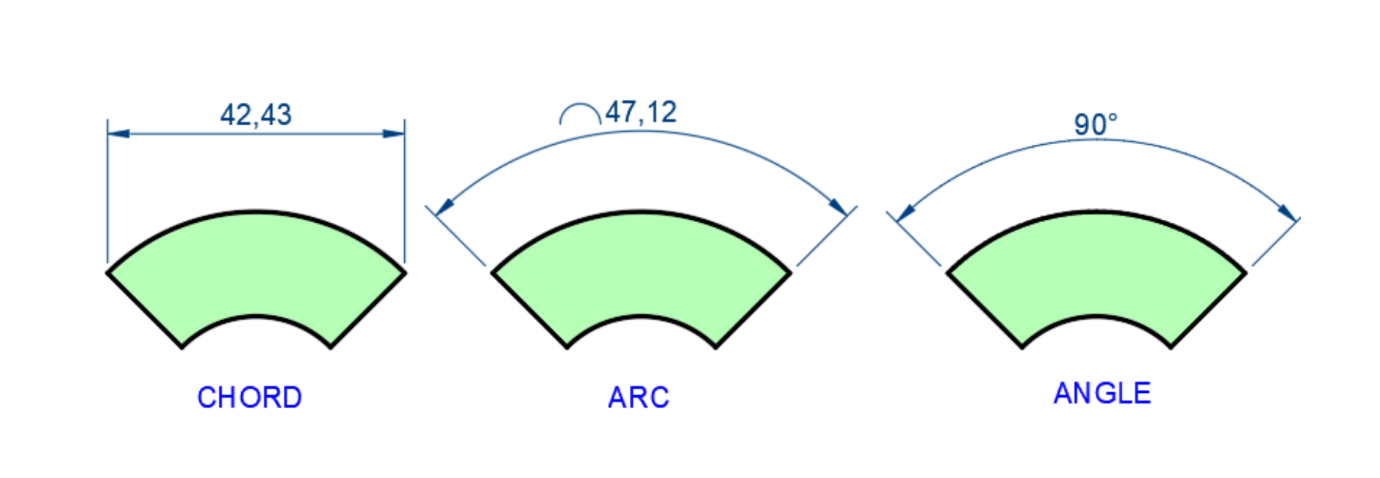
Arc / Chord
-
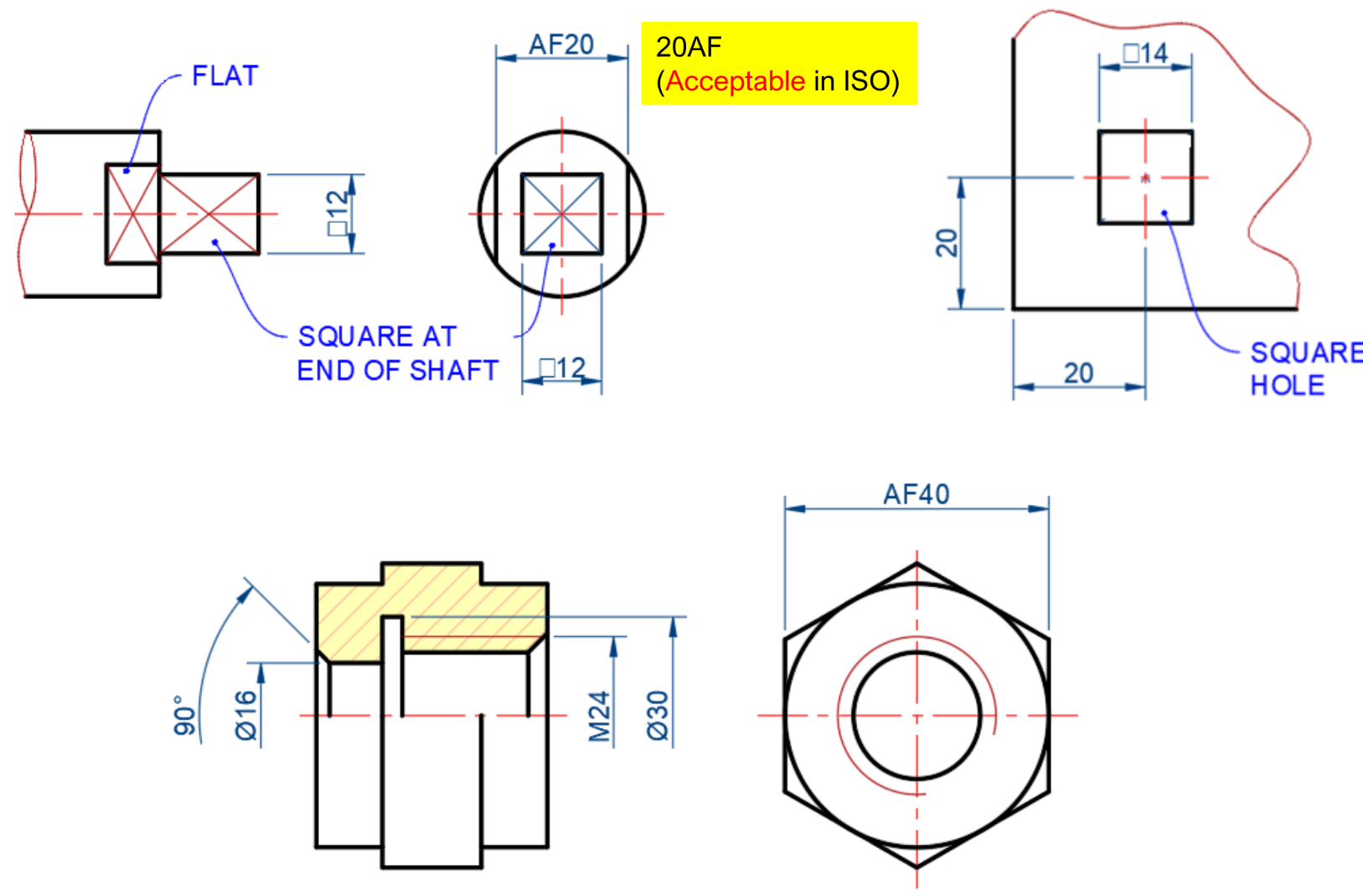
Square / flat
-
Undercut
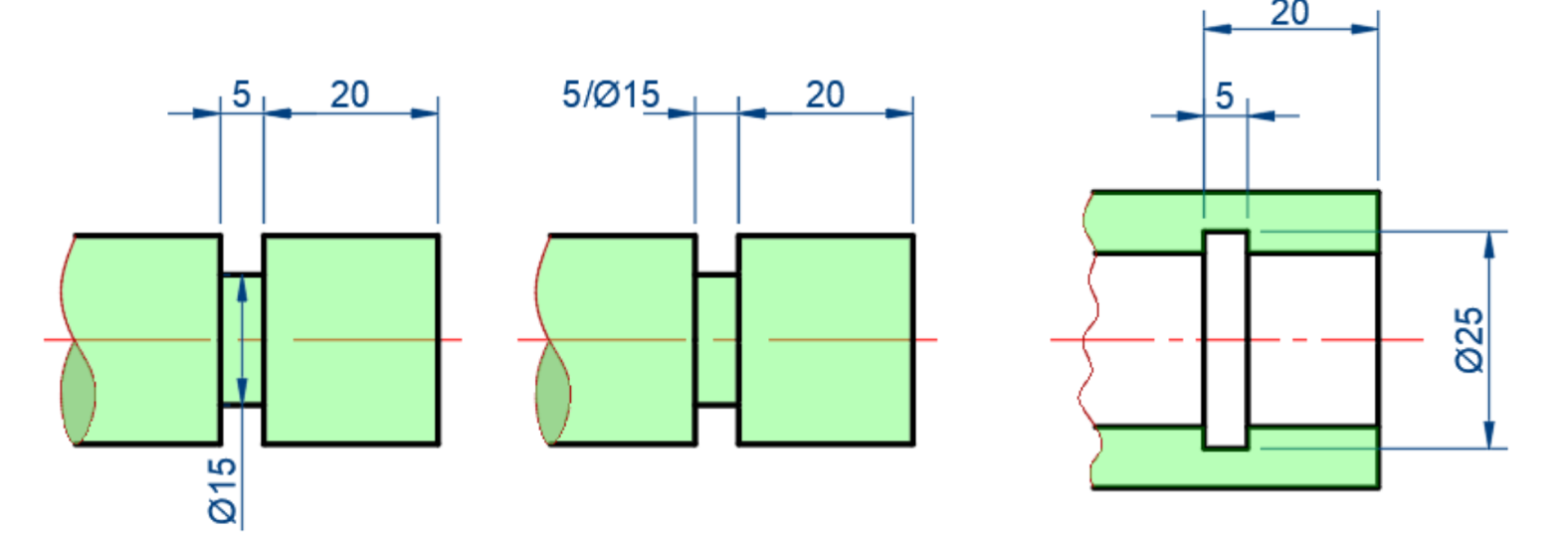
-
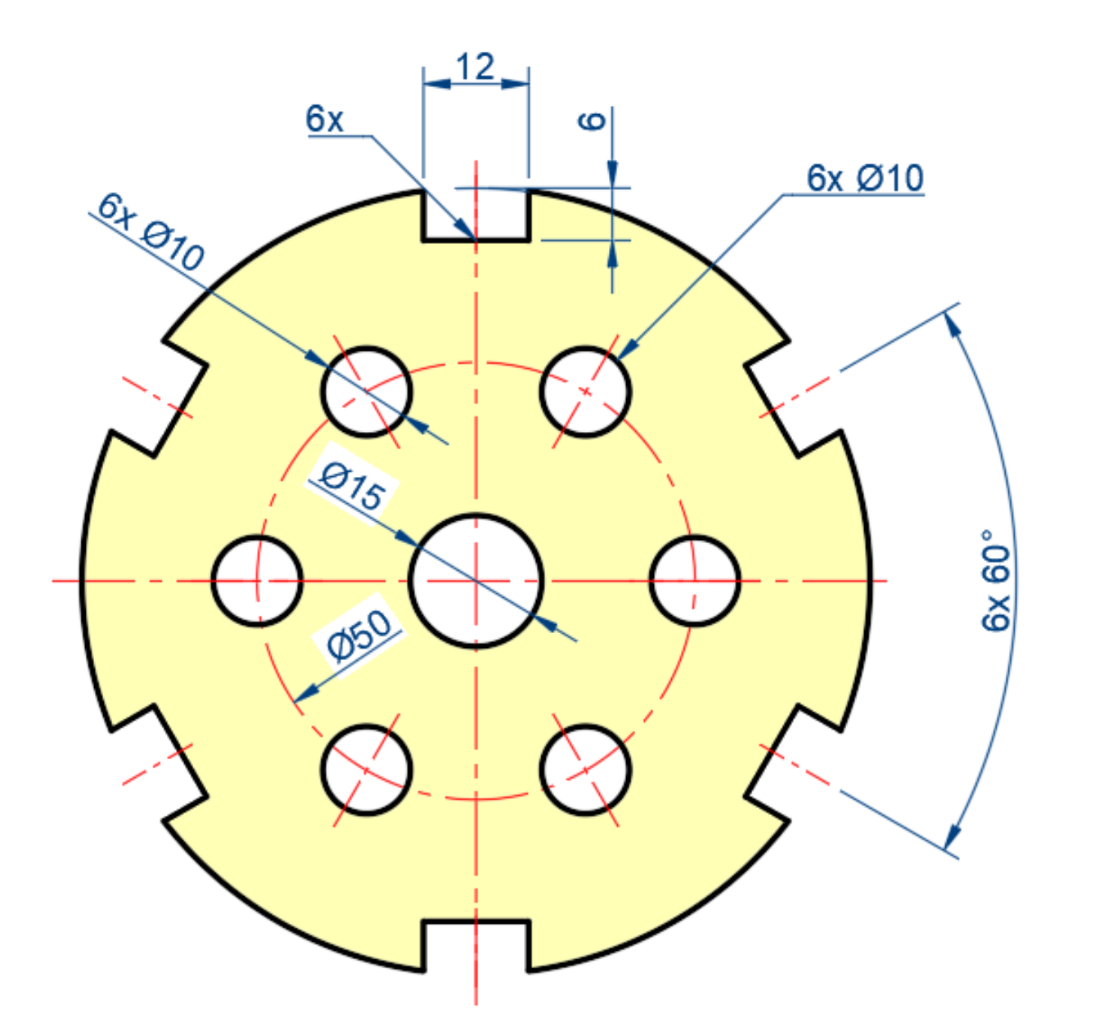
Equally spaced repeated
Dimensioning practices (ISO R129)
- R for arcs (<180) — for circles (>180) — SR/ for spherical radius / diameter
- Don’t dimension hidden lines — pick views that show it’s true size and shape
- Dimension on views that show the contour
- Ensure all dimensions are accounted for — avoid over/under dimensioning
- Only angles have units
- Reference dimensions require parenthesis (xx)
- Locate circular features by dimensioning to centerline
- Use centerline for symmetry
- Dimension circles on side view > front view for clarity
Dimensioning appearance (ISO R129)
- Value should be written above dimension line — with offset
- Put values/arrows outside extension line if not enough space
- Dimensions should be outside the view — unless it improves clarity
- Extension lines should have a visible gap from view and extend beyond dimension line
- Extension and Dimension lines should not cross
- Extension lines can cross
- Line up dimension lines as much as possible
- Extension lines & notes should be drawn nearest to point of interest